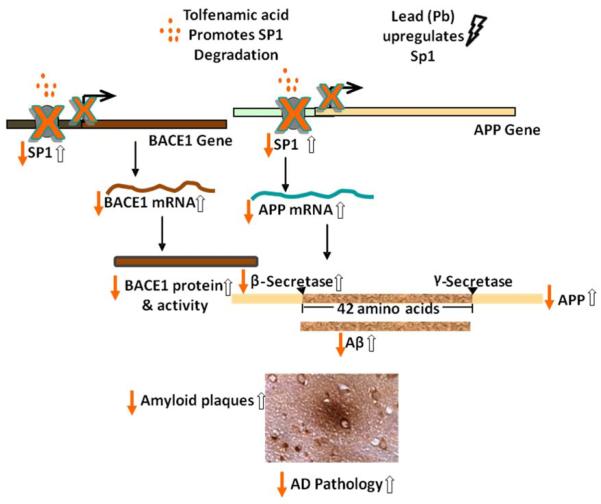
Figure 1. Downregulation of BACE1 and APP by tolfenamic acid and their upregulation by early Pb exposure.
Tolfenamic acid stimulates the degradation of the transcription factor Sp1, which reduces the transcription of APP and BACE1, consequently reducing the expression of BACE1 and APP as well as the aggregative product Aβ and the associated AD pathology. On the other hand, studies from our lab have revealed that Pb exposure early in life upregulates the expression of Sp1, APP, BACE1, Aβ and induces AD like pathology later in life. The solid arrows represent the hypothetical consequences following tolfenamic acid exposure, whereas the hollow arrows represent the latent effects after Pb exposure.