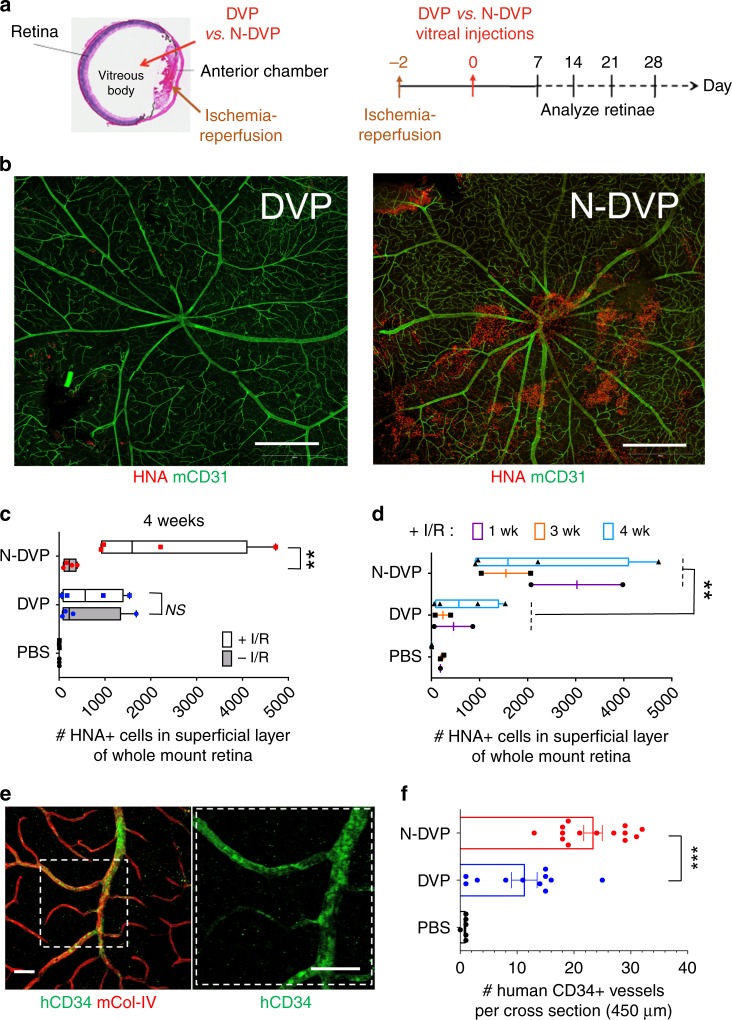
Fig. 6. Survival and vascular engraftment of primed vs. naïve DVP in I/R-injured murine retinae.
a Schematic of NOG mouse ocular I/R experimental system for testing in vivo functionality of human primed DVP vs. N-DVP (modified from Park et al., 20147). (left) Anatomical structures where I/R (anterior chamber) and human DVP and N-DVP cell injections (vitreous body) were performed (left panel). (right) Timeline for I/R injury surgery, human DVP injections (Day 0), human cell survival and engraftment analysis. b Human DVP survival at the superficial layer of murine retina at 3 weeks following injection of 50,000 DVP or N-DVP into the vitreous of I/R-treated NOG mouse eyes. Flat whole-mounted retinae were stained with antibodies for human-specific HNA (red), and tile scanned by confocal microscopic imaging (10x objective, 9 × 9 tiles). Shown are representative whole retinal images with HNA+ cells from primed DVP cell-injected (left panel) vs. N-DVP cell-injected (right panel) eyes. Scale bars = 500 μm. c Quantitation of HNA+ cells detected in the outer superficial layers of whole mount retinae following treatment of eyes with and without I/R, and injected with either primed DVP or N-DVP at (c) 4 weeks or (d) at 1, 3, and 4 weeks following DVP vs. N-DVP vs. control saline (PBS) injections, in eyes treated with and without I/R injury. Shown are the mean numbers from independent eye experiments of total HNA+ cells counted with imaging software per superficial layer of each whole-mounted retinae (whole field). **p < 0.01 (Mann-Whitney tests). e, f Human vascular engraftment into murine vessels. Whole-mounted retinae of I/R-injured eyes 2 weeks following DVP vs. N-DVP vs. PBS injections were immunostained with human CD34 (hCD34) to detect human endothelial engraftment. Antibodies for murine collagen type-IV (mCol-IV) were also employed to detect murine blood vessel basement membrane, and murine CD31 (mCD31) to detect murine endothelium. f The number of CD34+ human-murine chimeric vessels per 450 μm cross-section was quantitated via confocal microscopy and imaging software. Shown are results of independent measurements. ***p < 0.001 (unpaired t-tests).