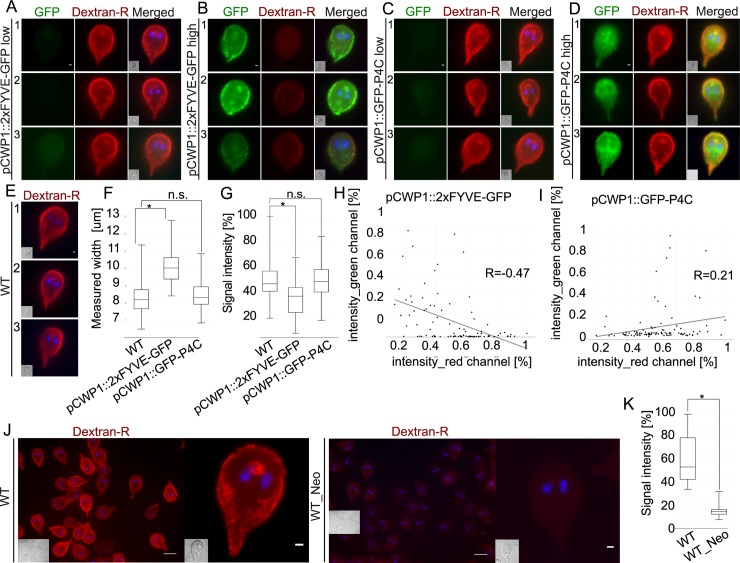
Fig 3. Depletion of free PI(3)P, PI(4,5)P2 and PI(3,4,5)P3 binding sites in G. lamblia trophozoites elicits uptake and morphological phenotypes.
(A-D) Light microscopy-based immunofluorescence analysis of representative transgenic trophozoites expressing Legionella-derived PIP-binding constructs. (A-B) Compared to low 2xFYVE-GFP-expressing cells from the same population, reduction of PI(3)P binding sites in cells highly expressing a regulated encystation-dependent epitope-tagged construct 2xFYVE-GFP (GFP) inhibits uptake of fluid-phase marker Dextran-R. Scale bars: 1 μm. (C-D) Expression levels of PI(4)P-binding epitope-tagged construct GFP-P4C expression (GFP) have no visible impact on Dextran-R signal at PVs of transfected cells. Scale bars: 1 μm. (E) Dextran-R uptake in non-transgenic wild-type cells as negative controls for construct-induced uptake phenotypes. Scale bars: 1 μm (F) Box-plot representing the distribution of cell width (in μm) across at least 100 wild-type, 2xFYVE-GFP- and GFP-P4C- expressing cells selected in an unbiased fashion. A statistically significant (two-sided t-test assuming unequal variances, p<0.05) increase in median cell width with respect to non-transgenic cells is detected for 2xFYVE-GFP- but not GFP-P4C- expressing cells. Asterisks indicate statistical significance. n.s.: not significant. (G) Box-plot representing the distribution of measured Dextran-R signal intensity across at least 100 wild-type, 2xFYVE-GFP- and GFP-P4C- expressing cells selected in an unbiased fashion. A statistically significant (two-sided t-test assuming unequal variances, p<0.05) decrease in Dextran-R signal intensity, normalized to wild-type cells (100%), is detected for 2xFYVE-GFP- but not for GFP-P4C- expressing cells. Asterisks indicate statistical significance. n.s.: not significant. (H) A statistically significant (p<0.5) linear correlation exists between Dextran-R signal (x-axis, intensity_red channel [%]) and 2xFYVE-GFP expression (y-axis, intensity_green channel [%]) measured across 100 cells. (I) The apparent linear correlation between GFP-P4C expression (y-axis, intensity_green channel [%]) and Dextran-R signal (x-axis, intensity_red channel [%]) is not statistically significant (p<0.5). (J) Wide-field microscopy-based immunofluorescence analysis of the impact of neomycin treatment on Dextran-R uptake to deplete PI(4,5)P2 binding sites in non-transgenic wild-type cells. With respect to non-treated cells (WT; left panel), Dextran-R signal at PVs is visibly impacted in non-transgenic neomycin-treated cells (WT_Neo; right panel). Scale bars: 10 μm for full wide-field image, 1 μm for a single cell. (K) Box-plot representing the distribution of measured Dextran-R signal intensity across 100 wild-type cells, either untreated (WT) or treated with neomycin (WT_Neo). Neomycin treatment causes a statistically significant (two-sided t-test assuming unequal variances, p<0.05) decrease in Dextran-R signal. Scale bars: wide-field: 10 μm; single cells: 1 μm. For all images, nuclei are labelled with DAPI (blue). Insets: DIC images.