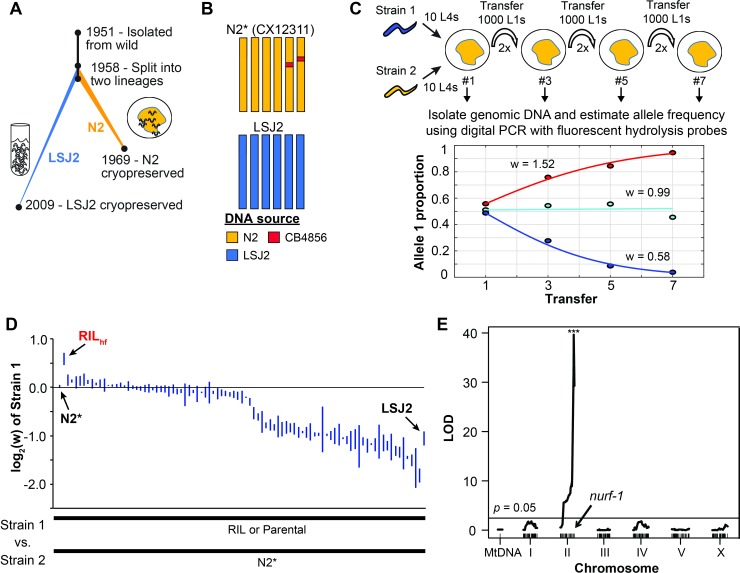
Fig 1. Competitive fitness measurements of N2*/LSJ2 RILs identifies an outlier RIL.
(A) Overview of the life history of two laboratory strains of C. elegans since their isolation from the wild in 1951 and subsequent split into two separate lineages around 1958. The standard reference N2 strain was cultured on agar plates seeded with E. coli bacteria until methods of cryopreservation were developed. LSJ2 was cultured in liquid, axenic media until 2009 when a sample of the population was cryopreserved. Resequencing of these strains identified ~300 genetic differences that fixed in one of the two lineages. (B) Schematic of two parental strains used in high-throughput analysis. N2* (or CX12311) is a near-isogenic line (NIL) containing ancestral alleles of two genes, glb-5 (chromosome V) and npr-1 (chromosome X) backcrossed from the CB4856 wild strain. Beneficial alleles in these two genes fixed in the N2 lineage; use of the N2* strain allows us to exclude the effects of these alleles from our studies. (C) Example data for three pairwise competition experiments used to quantify the fitness differences between two strains in laboratory conditions. Every odd generation, allele proportion is quantified using digital PCR and fluorescent hydrolysis probes (dots). These points are used to estimate the relative fitness of strain by fitting a haploid selection model to these points (line). In these conditions, outcrossing is expected to be very low or absent due to the lack of males in the initial population. (D) Relative fitness levels were measured for a panel of 89 RIL strains generated between N2* and LSJ2 by competing each RIL against N2* for seven generations. RILs were ordered by their average fitness value (3 replicates were performed for each). Parental strains were also assayed (N2* and LSJ2). RILhf (red) is highlighted for its unusually high fitness. (E) QTL mapping on the relative fitness differences between the RIL strains. A single significant QTL on the right arm of chromosome II, which overlaps the previously identified nurf-1 gene, was identified. Threshold line is significance level at p = 0.05 from a 1,000 permutation test.