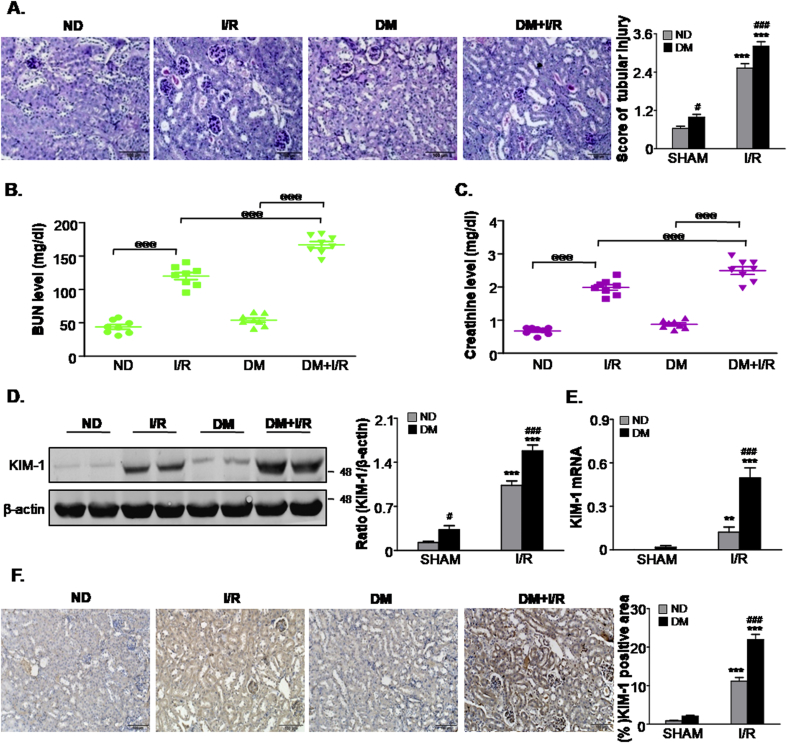
Fig. 1.
Diabetic mice are more susceptible to ischemic AKI.
A.Renal tissues stained with periodic acid-Schiff and quantification of tubular damage; B. BUN assay; C. Serum creatinine assay; D. Western blot analysis showing the protein expression of KIM-1; E. Detection of mRNA levels of KIM-1 by quantitative real-time PCR; F. Immunohistochemistry and quantitative analysis of KIM1; Scale bars = 100 μm. Data represent the mean ± S.E.M. for 6–8 mice. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared to SHAM group; #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 compared to ND group; @@@P < 0.001 as indicated in Fig. 1. ND: non-diabetic mice; DM: STZ-induced diabetic mice; I/R and DM + I/R: non-diabetic mice and STZ-induced diabetic mice were subjected to ischemia/reperfusion injury.