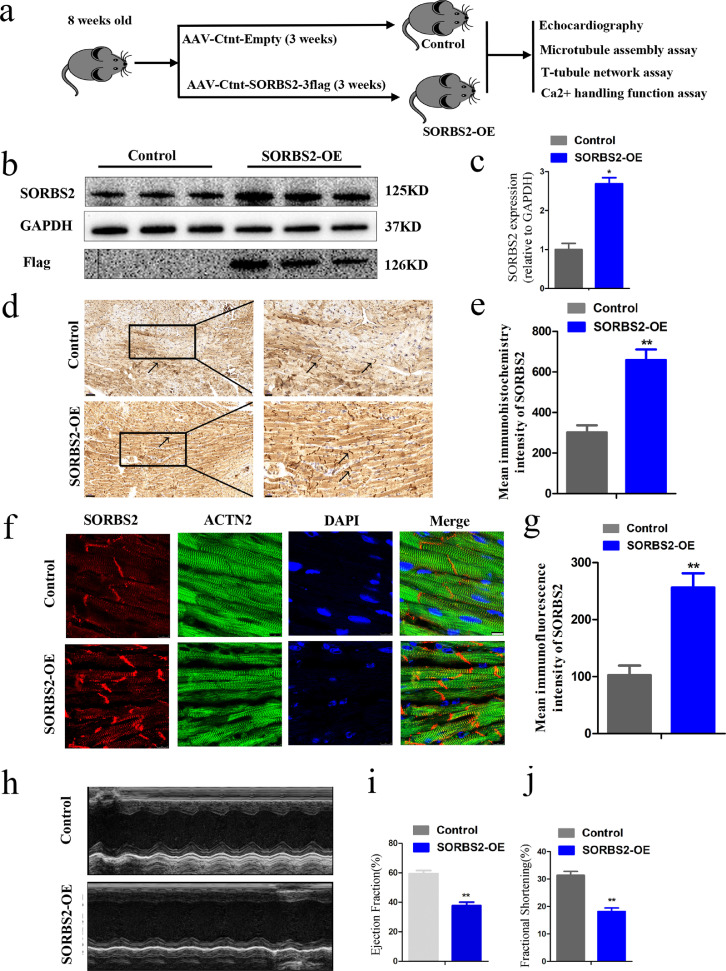
Fig. 6.
Establishment and verification of transgenic mice overexpressing SORBS2 in vivo. (a) flowchart in vivo. (b) and (c) Immunoblotting was used to assess the accumulation of the SORBS2 protein in cardiac tissues from harvested mice injected with control or SORBS2 overexpression AAV9 vectors. (n = 5 for each group, * p < 0.05; Student's t-test). Data shown as the mean ± SEM. (d) and (e) SORBS2 protein accumulation analyzed by immunohistochemistry staining; Black arrows represent SORBS2 localized in the Z-bands. The black box in the left panels indicates the areas enlarged in the right panels (scale bars represent 50 μm, 20 μm, respectively). Statistical analysis of the SORBS2 quantitative analysis levels in mice tissues. (n = 5 for each group, ** p < 0.01; Student's t-test). Data shown as the mean ± SEM. (f) and (g) Representative images of SORBS2 immunofluorescence staining of mice tissues (scale bars: 25 μm). Statistical analysis of the SORBS2 quantitative analysis levels in mice tissues. (n = 5 for each group, ** p < 0.01; Student's t-test). Data shown as the mean ± SEM. (h) Representative short-axis M-mode images of hearts from control and SORBS2 overexpression mice. (i) and (j) Ejection Fraction (EF) and Fractional Shortening (FS) of the control and SORBS2 overexpression mice were detected by Echocardiographic assessment. (n = 5 for each group, ** p < 0.01; Student's t-test). Data shown as the mean ± SEM. SORBS2-OE: experiment group (the wild-type C57 mice received AAV9-cTNT-SORBS2-3flag vector injections through jugular vein), Control: control group (the wild-type C57 mice received AAV9-cTNT-3flag vector injections through jugular veins).