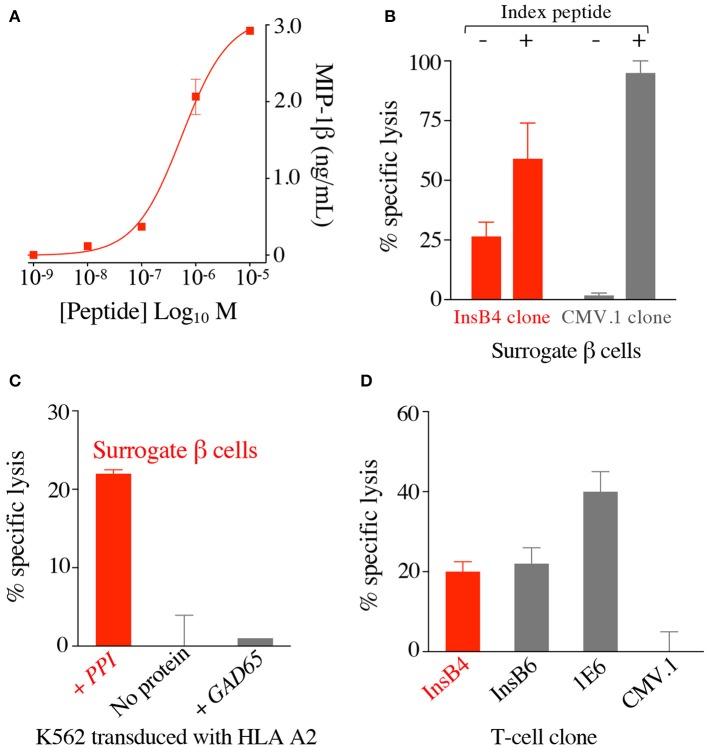
Figure 2.
T-cell clone InsB4 recognises a genuine HLA A2-restricted, insulin B-derived epitope presented at the surface of human pancreatic β cells. (A) HLA A2 restricted clone InsB4 grown from a patient with type 1 diabetes recognizes the peptide HLVEALYLV from insulin β chain. InsB4 tested with an increasing concentration of the HLVEALYLV peptide according to the x-axis. Performed in duplicate: overnight incubation and MIP-1β ELISA. Error bars depict SEM. (B) Surrogate β-cells (K562 transduced with HLA A2 and preproinsulin) were killed by the InsB4 clone. Chromium release cytotoxicity assay at a T-cell to target cell ratio of 3:1 over 5 h. CMV.1 (pp65 residues 495–503 from CMV) clone used as an irrelevant control. Exogenous index peptides (10−5 M) for each clone were included as positive controls for killing of the surrogate β-cells. Error bars depict SEM. (C) InsB4 specifically killed surrogate pancreatic β-cells as K562s transduced with HLA A2 alone or GAD65 (irrelevant protein) and HLA A2 were not recognised. Chromium release cytotoxicity assay at a T-cell to target cell ratio of 3:1 over 5 h. Performed in duplicate with error bars depicting SEM. Assay performed twice with similar results. (D) InsB4 and sister clone InsB6 (expressing the same TCR) kills real pancreatic cells. HLA A2 restricted clones 1E6 (preproinsulin (PPI) residues 15–24) and CMV.1 (pp65 residues 495–503 from CMV) were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Performed in duplicate with error bars depicting SEM.