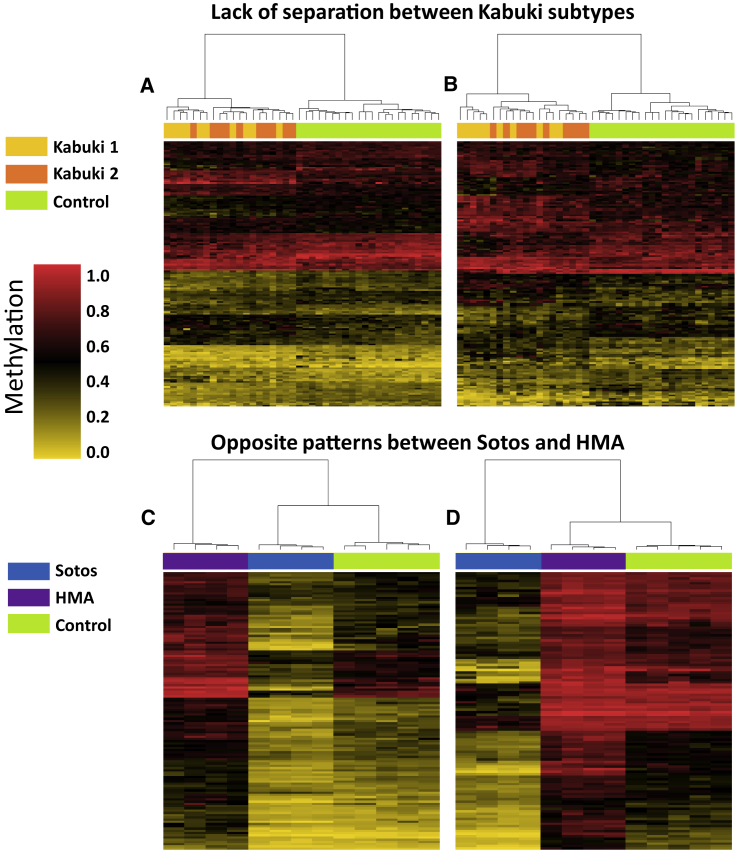
Figure 1.
Relationships across Various Syndromes and Their Subtypes
The plot shows clustering analysis with heatmap using probes specific to the DNA methylation of one syndrome (or its subtype) as compared with another. Rows indicate probes and columns indicate samples. The top pane colors indicate the classes. The heatmap color scale from gold to red represents the level of methylation from 0–1.
(A) Probes differentially methylated in Kabuki 1 (KMT2D) and controls do not provide distinction between subjects with Kabuki 1 and Kabuki 2 (KDM6A), although they differentiate both of them from the controls.
(B) The same pattern is observed when Kabuki-2-specific probes are used.
(C) Probes differentially methylated between individuals with Hunter McAlpine syndrome (HMA) (harboring duplication of NSD1) and controls generate a hypermethylation pattern in the HMA individuals. The same probes generate a mirror hypomethylation pattern in individuals with Sotos syndrome (loss of function of NSD1).
(D) The same mirror effect is observed when probes selected for Sotos syndrome are used.