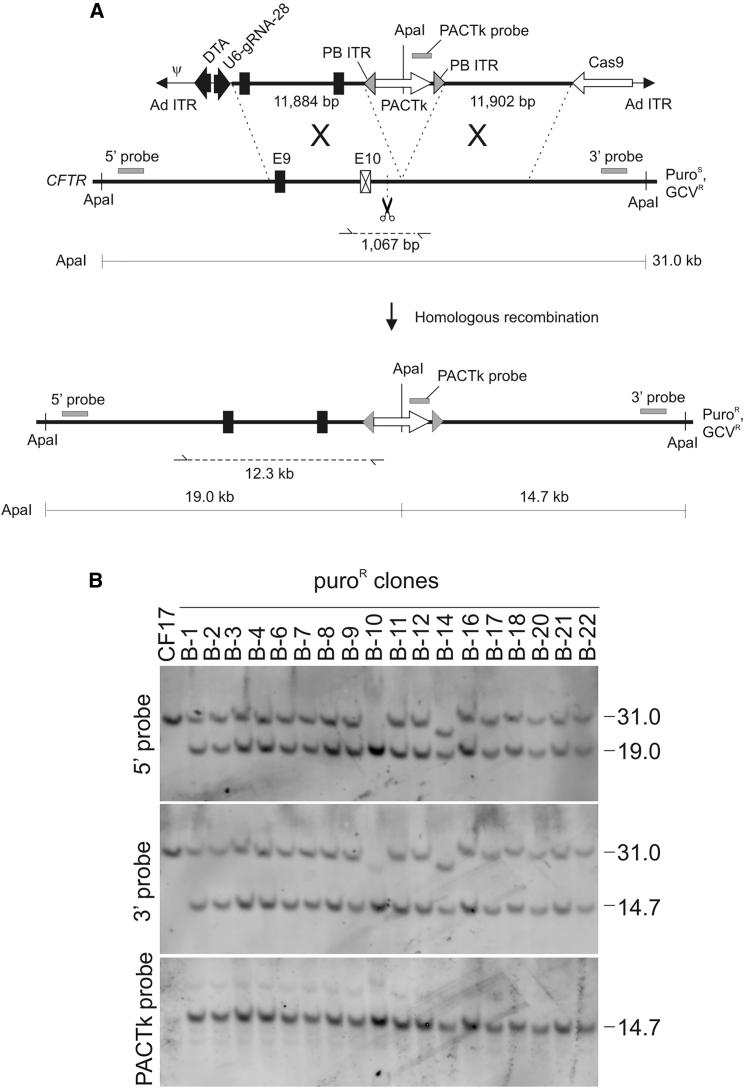
Figure 1.
Gene Targeting with All-in-One HDAd
(A) The all-in-one HD-23.8-CFTRm-PACTk-DTA+Cas9−28 possesses the donor DNA bearing a wild-type exon 10, a Cas9 expression cassette, and a gRNA expression cassette. The gRNA directs Cas9 cleavage 28 bp upstream of the PACTk insertion site indicated by the scissor. The 5′-CCA-3′ PAM in the donor was modified to 5′-TCA-3′ to prevent self-cleavage. PB inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) flank the PACTk cassette to permit its footprintless excision in the presence of PB transposase. Sizes of the diagnostic ApaI fragments and the locations of the 5′ external probe, 3′ external probe, and PACTk probe used for Southern blot analyses are shown. The 1,067-bp PCR product from the non-targeted allele is shown and was sequenced to determine its identity and the presence of indels. The 12.3-kb PCR product from the targeted allele is shown and was sequenced to determine whether the wild-type sequence was introduced into the target locus after gene targeting. The ΔI507 and ΔF508 mutations are 208 bp from the site of PACTk insertion. The position of the adenoviral packaging signal (ψ), adenoviral (Ad) ITR, and the diphtheria toxin A-fragment gene (DTA) for counter-selection against random integrations are shown for the HDAd. (B) Representative Southern blots of genomic DNA extracted from puroR colonies analyzed with the 5′ external probe, the 3′ external probe, and the PACTk probe.