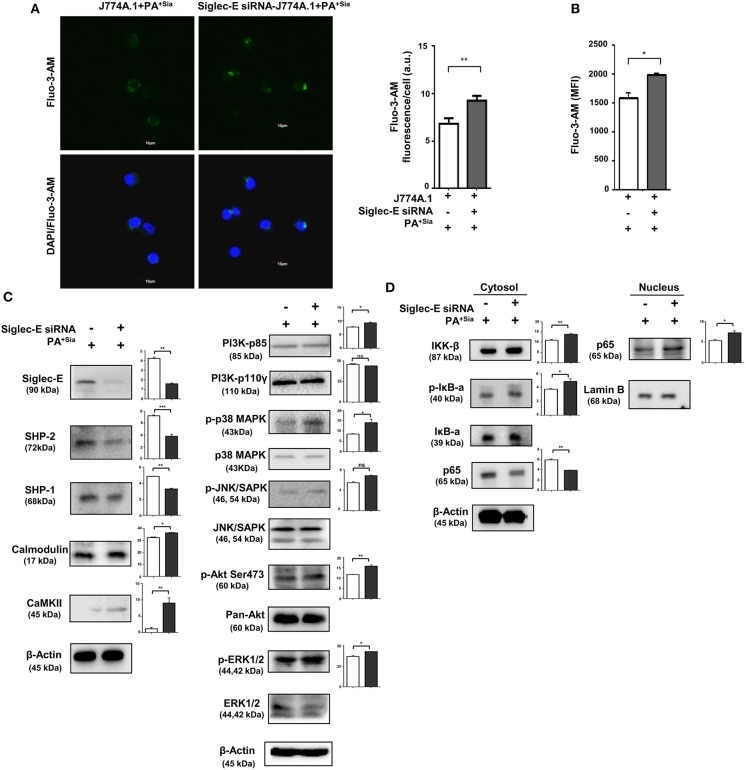
Figure 9.
Siglec-E silenced macrophages show enhanced intracellular calcium levels, calcium-related, MAPK and NF-κB signaling in response to PA+Sia. (A) Mock and siglec-E siRNA transfected J774A.1 cells were stained with Fluo-3-AM followed by PA+Sia infection for 15 min at 37°C. Cells were visualized by confocal microscopy as before. Microscopy images were representative of three independent experiments. Scale bar = 10 μm. (B) Intracellular calcium levels were detected by flow cytometric analysis of Fluo-3-AM stained macrophages following 15 min of 10 MOI PA+Sia infection at 37°C. MFI data from three independent experiments represented as mean ± s.e.m. (C) Expression of MAPK, ERK, JNK pathway molecules signaling molecules and calmodulin, calmodulin-dependent kinase type II was detected in lysates from PA+Sia-infected mock or siglec-E siRNA transfected macrophages by western blotting. (D) Similarly, infected macrophages were separated into cytosolic and nuclear fractions. Proteins were resolved in SDS-PAGE and probed for the expression of NF-κB signaling pathway to detect nuclear translocation of p65 subunit. Western blots (C,D) were representative of three independent experiments. Densitometric values reported are normalized with respect to β-actin band intensities and such values from atleast three independent experiments are used to calculate the mean band intensities which are presented as bar diagrams alongwith statistical significance of observed changes. Significance represented by *p ≤ 0.05 and **p ≤ 0.01.