Figure 6.
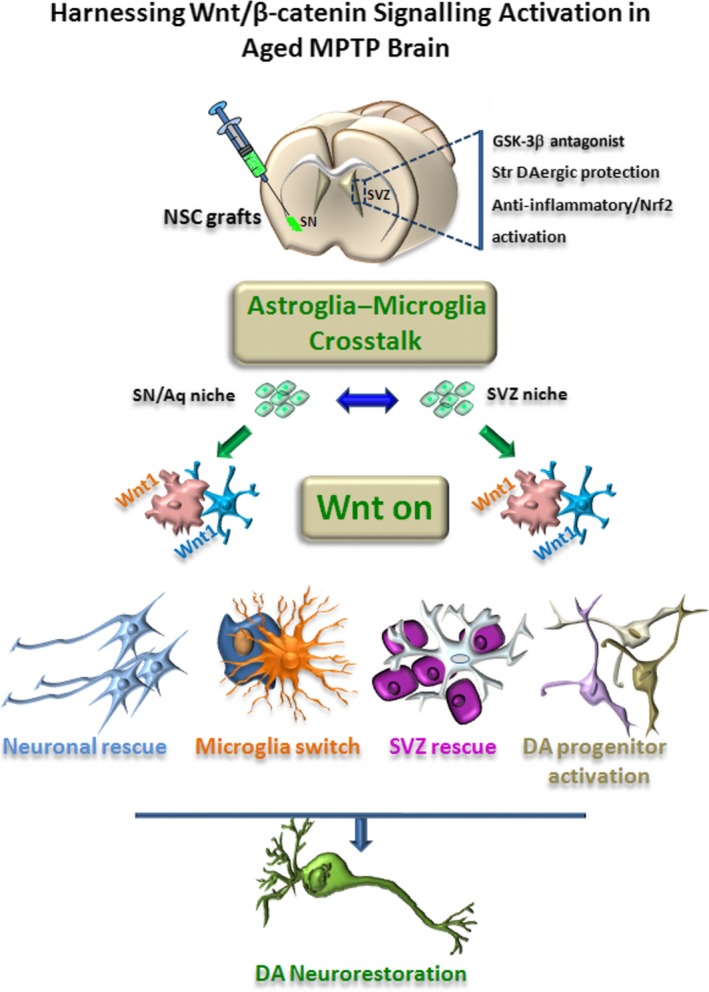
Harnessing WβC‐signalling activation in the aged, inflammed PD brain. Schematic representation of the ‘Wnt on' neurorestoration instructed by grafted NSCs in the aged PD brain. With age, the inflammed midbrain microenvironment coupled to dysfunctional astrocyte‐microglia interactions and environmental toxin exposure (MPTP) inhibit active Wnt‐signalling in astrocytes (“Wnt‐off” condition), resulting in exacerbation of inflammation and inhibition of Wnt‐dependent neuroprotective and pro‐regenerative capacities of astrocytes with harmful consequences for mDA neuron survival and repair from MPTP injury. NSCs, NSC‐derived astrocytes and endogenous astrocytes switch the inflammatory/Wnt‐genetic cascade via astrocyte‐neuron and astrocyte‐microglia crosstalk both at the SNpc and Aq‐PVR DA niche levels. Reciprocally, astrocyte derived Wnt1 further influence both exogenous and endogenous NSCs, reduce microglia pro‐inflammatory status, thus favouring beneficial effects for an overall TH neurorescue (“Wnt on”) program. Exogenous pharmacological treatments rescuing the impaired SVZ neurogenis (including GSK‐3β antagonists, anti‐oxidant and anti‐inflammatory drug treatment and DAergic activation promoting SVZ neurogenic rescue) are also illustrated
