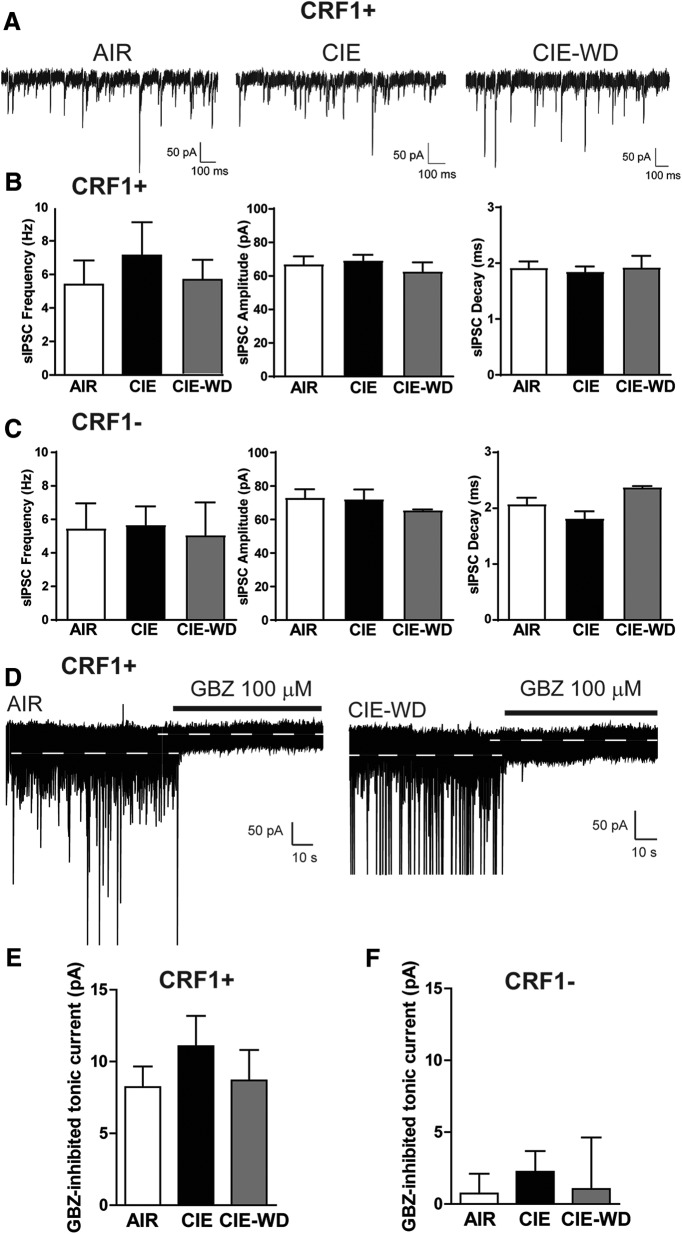
Figure 9.
Effects of chronic ethanol vapor on phasic and tonic inhibitory transmission in CRF1+ and CRF1− lateral amygdala neurons. A, Representative voltage-clamp recordings of CRF1+ neurons from AIR (left), CIE (center), and CIE-WD (right) mice. B, Summary of sIPSC frequency (left), amplitude (middle), and decay (right) in CRF1+ neurons from AIR, CIE, and CIE-WD mice. C, Summary of sIPSC frequency (left), amplitude (center), and decay (right) in CRF1− neurons from AIR, CIE, and CIE-WD mice. D, Representative voltage-clamp recording of CRF1+ cells from AIR (left) and CIE-WD (right) mice during GBZ superfusion (100 μm). White dashed line indicates the level of holding current before and after GBZ superfusion. E, Summary of tonic current revealed by gabazine superfusion in CRF1+ cells. F, Summary of tonic current revealed by gabazine superfusion in CRF1− cells.