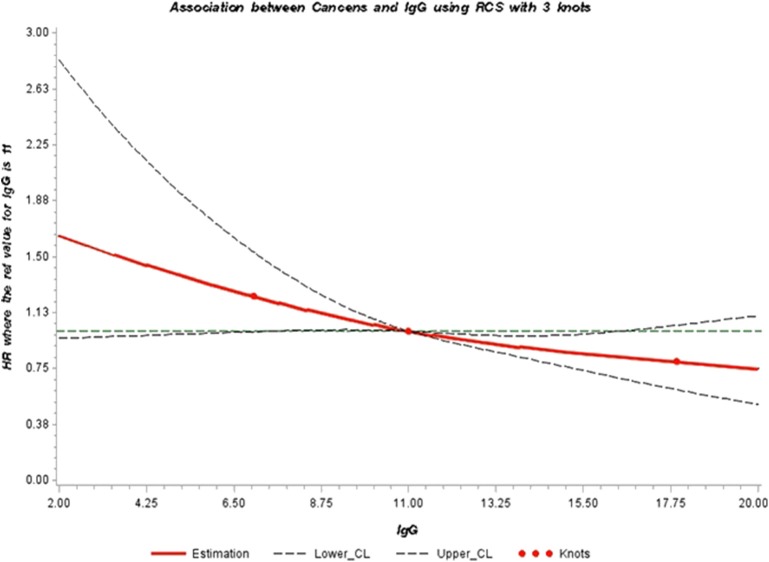
Figure 1.
Adjusted dose-response association between serum levels of IgG (g/L) and risk of pancreatic cancer (HR) using restrictive cubic splines. The direction of the hazard ratios observed in Tables 2, 3 was consistent with the shape of the curve, which presents a positive association for IgG levels lower than 11.00 g/L with pancreatic cancer risk (HR > 1.00) and a protective effect for high levels of IgG (11.00–20.00 g/L) (HR <1.00). However, the inverse association was only statistically significant for concentrations of IgG between 11.00 and 16.00 g/L.