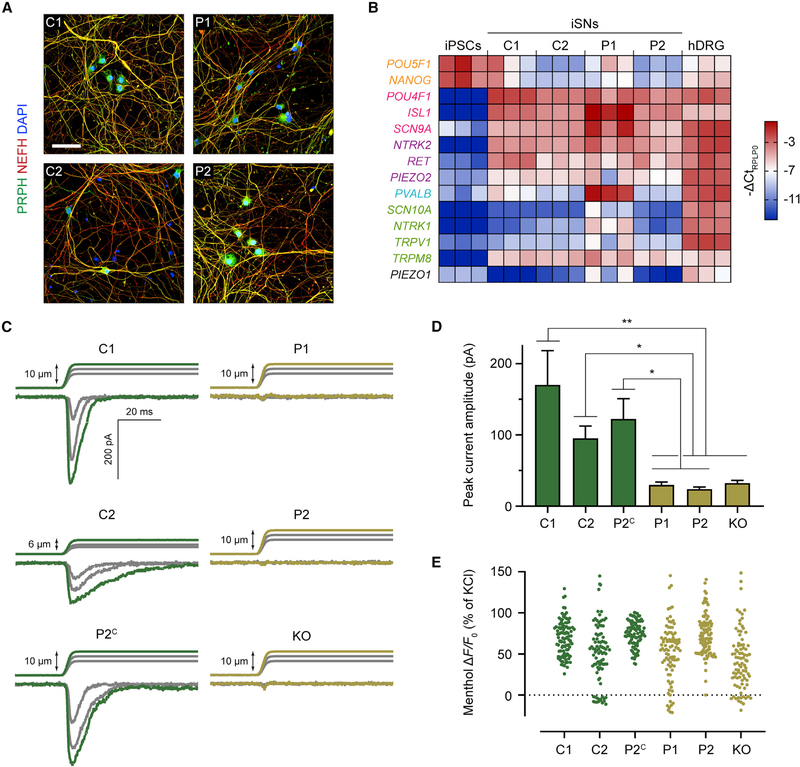
Figure 6. PIEZO2LOF iSNs Are Insensitive to Mechanical Stimuli.
(A) Representative immunocytochemistry from at least three differentiations of control and patient iSNs. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(B) qRT-PCR of sensory-related genes in day 21 iSNs, normalized to the housekeeping gene RPLP0 and expressed as −ΔCt for color coding. Each column represents an independent sample, three samples per cell line. Human DRG (hDRG) total RNA was used as a positive control, and WTC11 iPSCs were used as a negative control. Text color denotes gene category: orange, pluripotency; magenta, pan-sensory; purple, LTMR; blue, proprioceptor; green, nociceptor and/or thermoreceptor.
(C) Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings of iSNs during mechanical stimulation. Traces are examples from n = 10 neurons for each cell line.
(D) Quantification of mechanically activated current peak amplitudes in n = 10 cells per cell line. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Post hoc comparisons with Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’s correction for multiple comparisons. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
(E) Scatter dot plot for peak ΔF/F0 of individual cells after exposure to 500 μM menthol, normalized to KCl response. For each cell line, ≥80 cells were analyzed. In post hoc comparisons between each sample with one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s correction for multiple comparisons, no comparison was significantly different (p > 0.05).
See also Figures S4–S7 and Table S2.