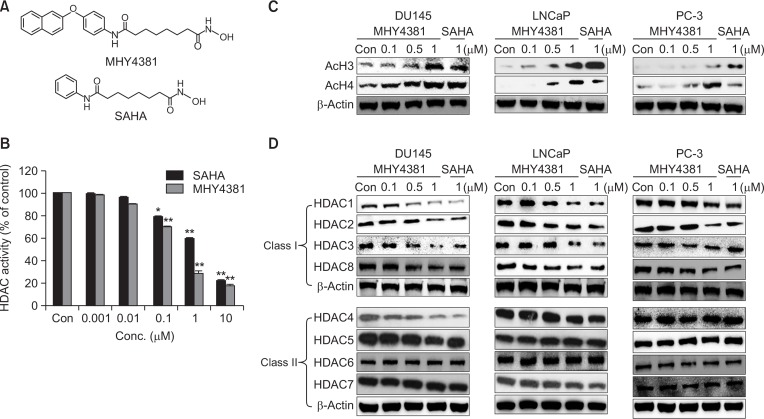
Fig. 1.
Effect of MHY4381 and SAHA on histone deacetylase (HDAC) expression and activity and acetylation of histones (H3 and H4). (A) The chemical structures of MHY4381 and SAHA. (B) HDAC enzyme activity was measured using a fluorogenic HDAC assay kit. HDAC enzyme activity is shown relative to that of the control. Three independent experiments were performed and results are expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance, followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 indicate significant differences between the control and treatment groups. (C) Effect of MHY4381 and SAHA on the levels of acetylated H3 and H4. Prostate cancer (DU145, LNCaP, and PC-3) cells were exposed to the indicated concentrations of MHY4381 and SAHA for 48 h. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (D) Effect of MHY4381 and SAHA on the protein expression levels of HDACs. Prostate cancer (DU145, LNCaP, and PC-3) cells were exposed to the indicated concentrations of MHY4381 and SAHA for 48 h and expression of HDACs (class I and II) was measured by western blot analysis. β-Actin was used as a loading control.