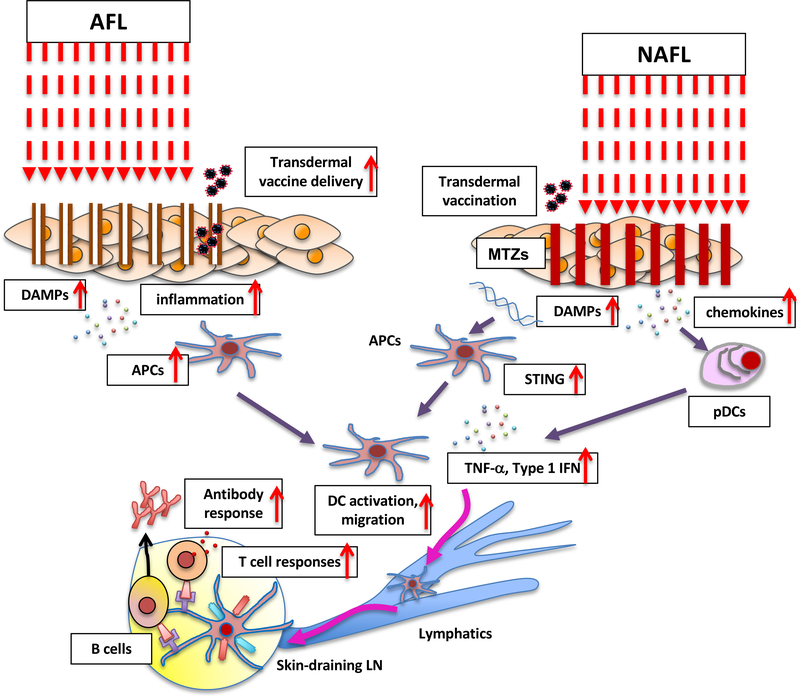
Figure 2. The mechanism of action of the AFL and NAFL adjuvants.
AFL skin treatment induces the mild inflammatory milieu created by a narrow layer of coagulated dead tissue around each micro-channel. The efficient delivery of transdermal vaccine to skin DCs is also facilitated by the micro-channels. The NAFL treatment induces skin cell death (called microthermal treatment zones, MTZs) releasing damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) including dsDNA and micro-sterile inflammation array. dsDNA is taken up by antigen presenting cells (APCs) and recognized by intracellular pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). PRRs then transduce signals to STING activating IRF3 and NF-κB. Type I interferons, proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines are produced to enhance the maturation and migration of APCs. AFL treatment also induces expression of chemokines in the skin. These chemokines recruit plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) from circulation system into the skin. The pDCs release a number of factors to enhance the maturation and migration of APCs.