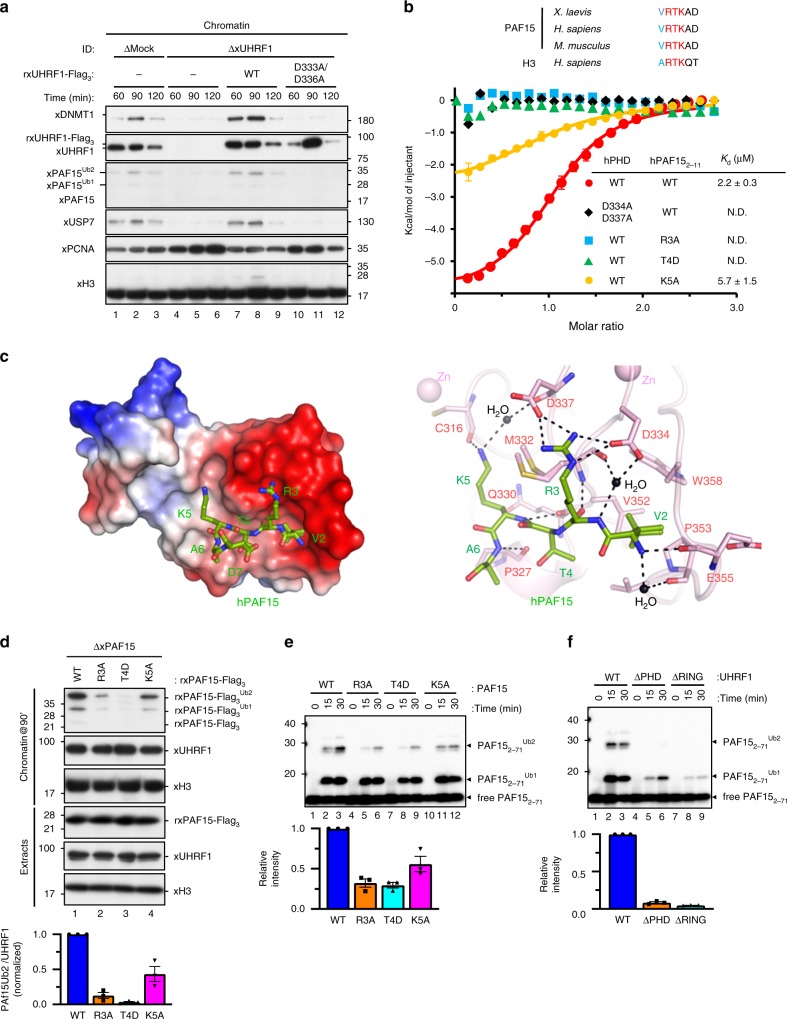
Fig. 2. UHRF1 recognizes and ubiquitylates the N-terminal H3-like sequence of PAF15.
a Mock-depleted or UHRF1-depleted extracts were supplemented with the indicated recombinant proteins (wt/D333A/D336A xUHRF1; see “Methods”) and chromatin was isolated. Chromatin-bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. For the protein levels of each protein in the extracts, see Supplementary Fig. 2a. b Comparison of the N-terminal sequence of PAF15 and histone H3 across different species. Residues mutated in the PAF15 mutants used in this study are shaded. Superimposition of plots of enthalpy changes in the interaction between hPHD and hPAF152-11 peptides by ITC measurement. c Recognition of the N-terminus of hPAF15 by hPHD. The left panel shows the crystal structure of PHD in complex with hPAF15. hPHD as a surface model with electrostatic potential (red, negative; blue, positive). The right panel shows recognition of PAF15 N-terminus (green stick model) by hPHD (pink stick model). Hydrogen bonds and water molecules are shown as black lines and balls, respectively. d PAF15-deleted extracts were supplemented with wild-type PAF15-Flag3 and its variants (R3A, T4D, and K5A). After the addition of sperm chromatin, chromatin-bound proteins were isolated after 90 min and analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. The level of PAF15Ub2 on chromatin was quantified for each set of conditions as explained in the “Methods” section. e, f In vitro ubiquitylation assay using the indicated hUHRF1 E3-ligases and hPAF15 substrates. Lower panels show the relative intensity of the band corresponding to dual mono-ubiquitylated PAF15. Bars represent the means of three independent experiments with SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.