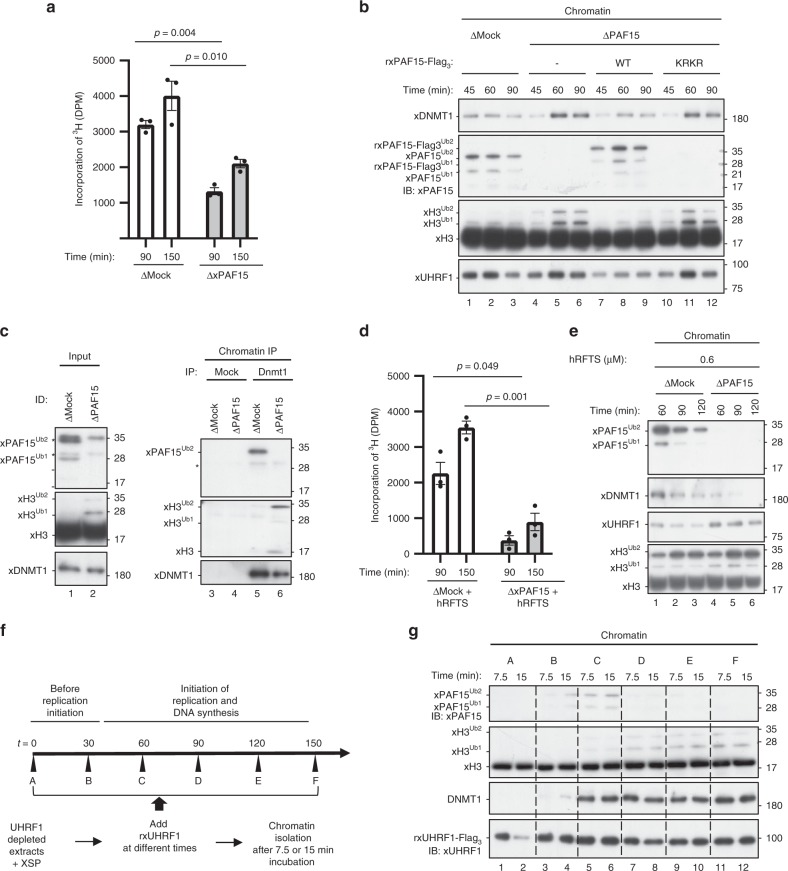
Fig. 4. xPAF15Ub2 promotes recruitment of xDNMT1 and maintenance of DNA methylation.
a, d Sperm chromatin was added to either mock- or xPAF15-depleted extracts containing radiolabeled S-[methyl-3H]-adenosyl-L-methionine in the absence (a) or presence of 0.6 μM hRFTS (e). The efficiency of DNA methylation was measured at the time points indicated. Bar graphs depict the quantification of incorporated SAM into genomic DNA with mean and SEM from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined using Student’s t test. b, e Sperm chromatin was added to mock- or xPAF15-depleted interphase extracts in the absence (b) or presence (f) of hRFTS. PAF15-depleted extracts were supplemented with either buffer alone (lanes 4–6), purified wild-type xPAF15-Flag3 or K18R/K27R(KRKR) mutant xPAF15-Flag3 (320 nM final concentration, lanes 7–9 or 10–12, respectively) in the experiment described in b. At the indicated time points, chromatin fractions were isolated and subjected to immunoblotting using the antibodies indicated. For the PAF15 levels in extracts, see Supplementary Fig. 2a. c Sperm chromatin was replicated in mock- or PAF15-depleted interphase egg extracts. Isolated and solubilized chromatin proteins were subjected to immunoprecipitation using an anti-xDNMT1 antibody. The resultant immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. Asterisks, non-specifically detected proteins. f Schematic of experimental approach to test the differential regulation through UHRF1 during the progression of S phase. g Sperm chromatin was added to xUHRF1-depleted extracts and incubated for 0, 30, 60, 90, 120, or 150 min. Extracts were then supplemented with recombinant xUHRF1-Flag3 and further incubated for 7.5 or 15 min. Chromatin fractions were isolated and chromatin-bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using the antibodies indicated. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.