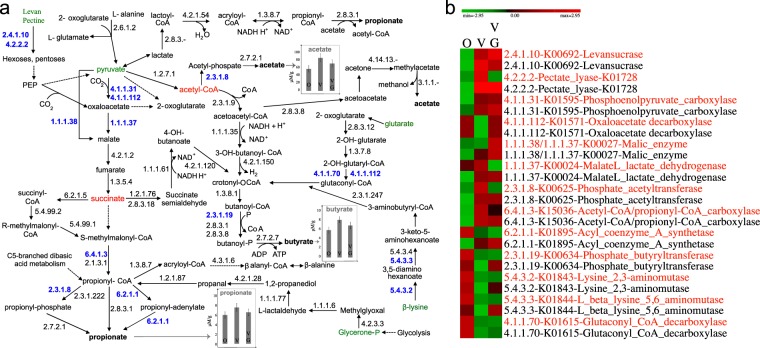
Figure 3.
Reconstruction of microbial pathways in the intestine involved in the biosynthesis of short-chain fatty acids (acetic acid, butanoate and propionate) (SCFAs) using DESeq statistically significant differences for genes and proteins identified from the multi-omics data sets belonging to omnivores (O), vegans (V) and vegetarians (VG). Panel a, schematic representation of the SCFA metabolic pathways. The blue numbers indicate enzymes that were differentially (FDR < 0.05) detected among diet groups. Principal metabolites are colored in green. The average concentrations (µM/g of feces) of acetate, butyrate and propionate found in the metabolome of omnivores, vegans and vegetarians are indicated in the histograms. Panel b, heatmap showing the differentially detected genes (red characters) and proteins (black characters) in the diet groups. The colors of the scale bar denote the abundance of the genes and proteins (indicated in blue characters in panel a), with 1.94 indicating the highest abundance (red) and −1.94 indicating the lowest abundance (green) between diet groups.