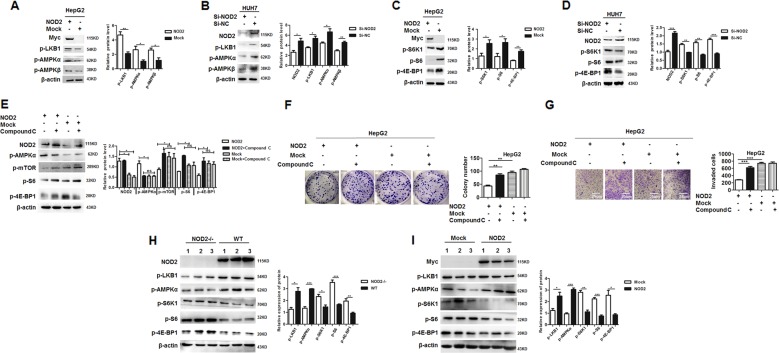
Fig. 4. NOD2 inhibited HCC progression through activating AMPK signaling pathway.
a HepG2 cells were transfected with NOD2 plasmid or mock control plasmid, and further cultured for 24 h. Activation status of AMPK pathway, including p-LKB1, p-AMPKα and p-AMPKβ were detected by western blot. b HUH7 cells were transfected with Si-NOD2 or Si-NC, and the activation status of AMPK pathway was detected by western blot. c HepG2 cells were transfected with NOD2 plasmid or mock control plasmid, and the activation status of mTORC1 pathway, including p-S6K1, p-S6 and p-4E-BP1 were detected by western blot. d HUH7 cells were transfected with the mixture of two SiRNAs against NOD2 (Si-NOD2), and the cells transfected with random sequences (Si-NC) acted as a mock control. Activation status of mTORC1 pathway was detected by western blot. e–g HepG2 cells were transfected with NOD2 plasmid, and further cultured for 6 h before compound C (10 μM) was added to inhibit the activation of AMPK pathway. Western blot assay was performed to detect the expression of NOD2, p-mTOR, p-AMPKα, p-S6K1, p-S6 and p-4E-BP1 after the transfection (e). Colony formation (f) and invasion (g) of the NOD2-transfected HCC cells with compound C treatment were analyzed. h NOD2-/- and WT mice were injected with DEN and CCl4 to induce hepatocellular carcinoma, and western blot assay was performed to detect the AMPK-mTORC1 pathway activation in the liver tissues from the NOD2-/- and WT mice. i HCC cells were injected to the nude mice to construct the xenograft tumor models as described before. When visible tumor appeared, the mice were divided into NOD2-transfected group and the mock control group. Relative expression of the related signaling transduction pathway proteins, including AMPK pathway related proteins and mTORC1 pathway related proteins were detected by western blot. The densities of all bands were analyzed by Image J software and statistically analyzed by GraphPad software. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 for statistical analysis of the indicated groups.