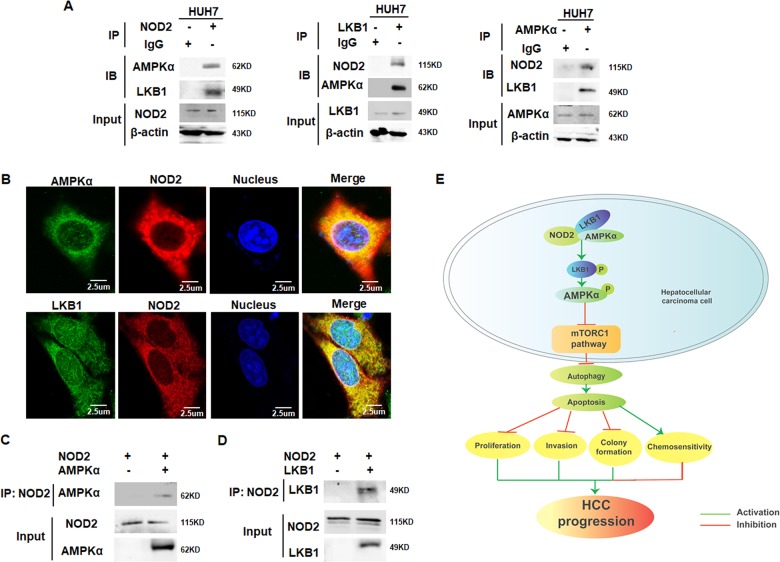
Fig. 6. NOD2 promoted activation of AMPK signaling pathway through directly binding with LKB1-AMPKα complex.
a HUH7 cells were cultured for 24 h before cell lysate was obtained for IP assay. The endogenous interaction between NOD2 and LKB1/AMPKα (left panel), LKB1 and NOD2/AMPKα (middle panel) as well as AMPKα and NOD2/LKB1 (right panel) were detected by IP assay by using the indicated antibodies. b HUH7 cells were cultured in 24-well plate for 24 h before the cells were fixed and stained with primary antibodies against NOD2 and AMPKα/LKB1, followed by staining with fluorescence-conjugated secondary antibodies (red for NOD2, green for AMPKα or LKB1). DAPI was used to stain the nuclei, and the co-localization between NOD2 and AMPKα/LKB1 was visualized as yellow fluorescence in the merged panel. c–d NOD2, AMPKα and LKB1 proteins were obtained from the in vitro translation system. NOD2 protein was mixed with AMPKα or LKB1 protein, and the direct binding between NOD2 and AMPKα (c), NOD2 and LKB1 (d) were detected by IP assay. All figures presented are representative data from at least three independent triplicate experiments. e The working model showing the role and mechanism of NOD2 in HCC cells. NOD2 directly binds with LKB-AMPKα complex and further activates LKB1-AMPKα pathway, which leads to inhibition of the mTORC1 pathway and activation of autophagy-mediated apoptosis in HCC cells; thus finally reverses the malignant behaviors of HCC cells and enhances the chemosensitivity of HCC cells to sorafenib, lenvatinib and 5-FU. Altogether, NOD2 acts as a tumor suppressor in HCC cells and loss of its expression in clinical HCC patients promotes HCC progression.