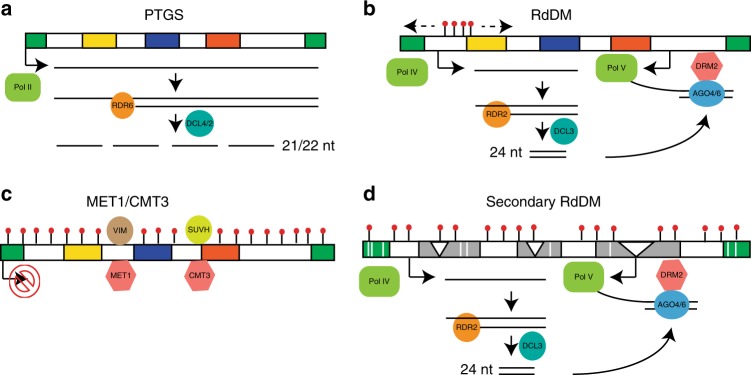
Fig. 5. Model of LTR silencing.
a In early stages, LTR is transcribed by RNA Pol II. Post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS) is triggered with double-stranded RNA synthesis by RDR6 and afterwards 21-22nt sRNA generation by DCL4 and/or DCL2. b Along with increase of LTR copy number, 24nt sRNA is produced starting from certain region of LTR (gag for example) by RNA Pol IV, RDR2 and DCL3. These 24nt sRNAs are recruited into AGO4/6 which interact with DNA methyltransferase DRM2. By sequence pairing between 24nt sRNA and Pol V transcript, AGO-DRM2 complex function in cis to methylate LTR which is called RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM). RdDM then spreads to more regions of LTR. c After established by RdDM, DNA methylation is maintained by RNA-independent mechanism: CG methylation is maintained by VIM and MET1, CHG methylation is maintained by KYP/SUVHs and CMT3. LTR is rarely transcribed. d Accumulated mutations in 5′ and 3′ LTRs and coding sequences (represented by white bars) together with TE re-insertion (represented by white triangles) make it less possible for LTR to transpose. At this stage, LTR is transcribed again and generates 24 nt sRNA, which mediates secondary RdDM.