Figure 2.
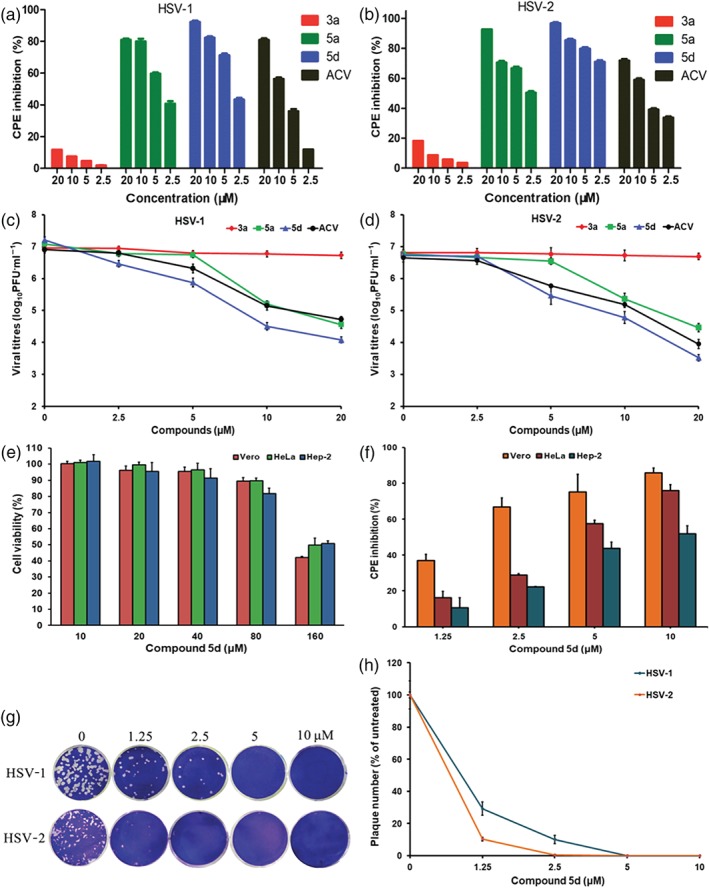
Effect of guanidine modification on the inhibitory effect of BS‐pyrimidine derivatives on herpes simplex virus (HSV)‐1 and HSV‐2. (a) HSV‐1‐infected or (b) HSV‐2‐infected (multiplicity of infection [MOI] = 0.1) Vero cells were treated with compounds 3a, 5a, 5d, or acyclovir (ACV; 2.5, 5, 10, and 20 μM) for 24 hr at 37°C. After that, the anti‐HSV effects were evaluated by cytopathic effect (CPE) inhibition assay. Results shown are means ± SD from six independent experiments. (c) HSV‐1 or (d) HSV‐2 (MOI = 1.0) was pretreated with compounds 3a, 5a, 5d, or ACV (2.5, 5, 10, and 20 μM) for 1 hr at 37°C before infection. Then, after adsorption, the media containing each compound were added to cells, respectively. At 24 hr p.i., the virus yields were determined by plaque assay. Values are means ± SD (n = 5). (e) After 48‐hr exposure to compound 5d at the indicated concentrations, the cell viability of Vero, HeLa, and Hep‐2 cells was measured by MTT assay, respectively. Values are means ± SD (n = 6). (f) HSV‐1 (MOI = 0.1)‐infected Vero, HeLa, and Hep‐2 cells were treated with compound 5d (1.25, 2.5, 5, and 10 μM) for 24 hr at 37°C. Then the antiviral effects were determined by CPE inhibition assay. Values are means ± SD (n = 5). (g) Approximately 100–200 PFU per well of HSV‐1 or HSV‐2 virus were pre‐incubated with compound 5d (0, 1.25, 2.5, 5, and 10 μM) for 1 hr at 37°C before infection, respectively. Then the virus–compound 5d mixture was transferred to Vero cells, incubated at 4°C for 1 hr and subjected to plaque reduction assay. (h) Plots of the plaque numbers from the plaque reduction assays performed on Vero cells infected with HSV and treated with the indicated concentrations of compound 5d (1.25, 2.5, 5, and 10 μM). Results shown are means ± SD from five independent experiments
