Figure 9.
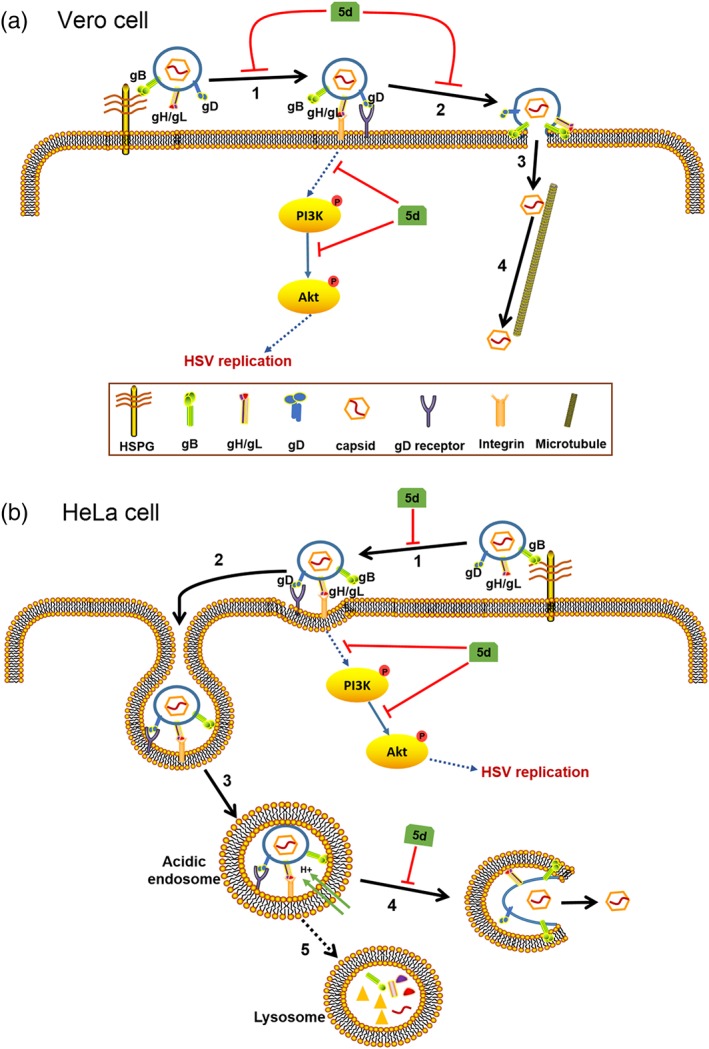
Mechanism of action of compound 5d in herpes simplex virus (HSV)‐infected Vero and HeLa cells. (a) In Vero cells, compound 5d may block the initial binding of HSV gB protein to cellular heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan (HSPG; 1) and interfere with the fusion process at plasma membrane (2), so as to inhibit the adsorption and entry process of HSV. compound 5d also inhibits the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway in early stage of HSV life cycle to reduce virus replication. (b) In HeLa cells, compound 5d may block the initial attachment of HSV particle to cellular HSPG (1) before gD protein binding to its receptor. After virus endocytosis (2), and endosomal acidification (3), compound 5d may block gB‐mediated fusion at endosomal membrane (4), so as to inhibit the capsid egress from endolysosome compartments. Compound 5d may also block the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway to inhibit subsequent virus replication
