Figure 6.
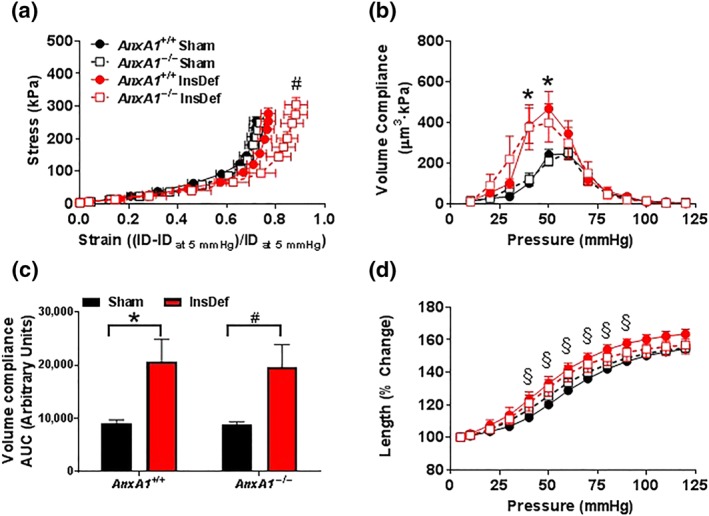
Effects of insulin deficiency on passive mechanical properties of vascular walls. (a) Stress–strain relationship; (b) volume compliance (over the pressurisation range) and (c) AUC for volume compliance; and (d) % change in length (over the pressurisation range) in sham AnxA1 +/+ (n = 14), sham AnxA1 −/− (n = 8), insulin‐deficient (InsDef) AnxA1 +/+ (n = 13), and insulin‐deficient AnxA1 −/− (n = 8) male mice. Values are mean ± SEM. # P < .05, significantly different from all other groups; * P < .05, significantly different from sham AnxA1 +/+, # P < .05, significantly different from significantly different from AnxA1 −/− sham mice, § P < .05, significantly different from AnxA1 +/+ insulin‐deficient mice. (a), (b), and (d) were analysed using repeated‐measures two‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc analysis, whereas (c) were analysed using two‐way ANOVA with Fisher's LSD post hoc analysis
