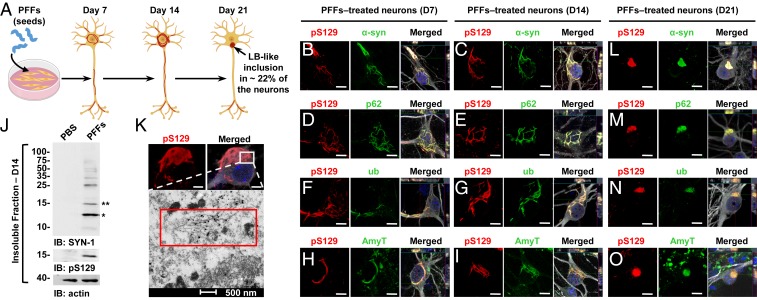
Fig. 1.
At early stage, α-syn–seeded fibrillar aggregates share the immunohistochemical but not the structural and morphological features of the bona fide human LBs. (A) Seeding model in primary hippocampal neurons. (B–I and L–O) Temporal analysis of α-syn aggregates formed at D7 (B, D, F, and H), at D14 (C, E, G, and I), and at D21 (L–O) in PFF-treated neurons. Aggregates were detected by ICC using either pS129 (81a) in combination with total α-syn (epitope: 1–20) (B, C, and L) or with the Amytracker dye (AmyT; H, I, and O) or pS129 (MJFR13) in combination with p62 (D, E, and M) or ubiquitin (F, G, and N) antibodies. Neurons were counterstained with MAP2 antibody and the nucleus with DAPI staining. (J) Western blot analysis. Total α-syn, pS129, and actin were detected by SYN-1, pS129 (MJFR13), and actin antibodies, respectively. Monomeric α-syn (15 kDa) is indicated by a double asterisk; C-terminal truncated α-syn (12 kDa) is indicated by a single asterisk; the higher molecular weights corresponding to the newly formed fibrils are detected from 25 kDa to the top of the gel. (K) At D14, pS129-positive aggregates imaged by confocal microscopy was then examined by EM after immunogold labeling. (Scale bars: B–I and L–O, 10 μm; K, Upper, 5 μm.)