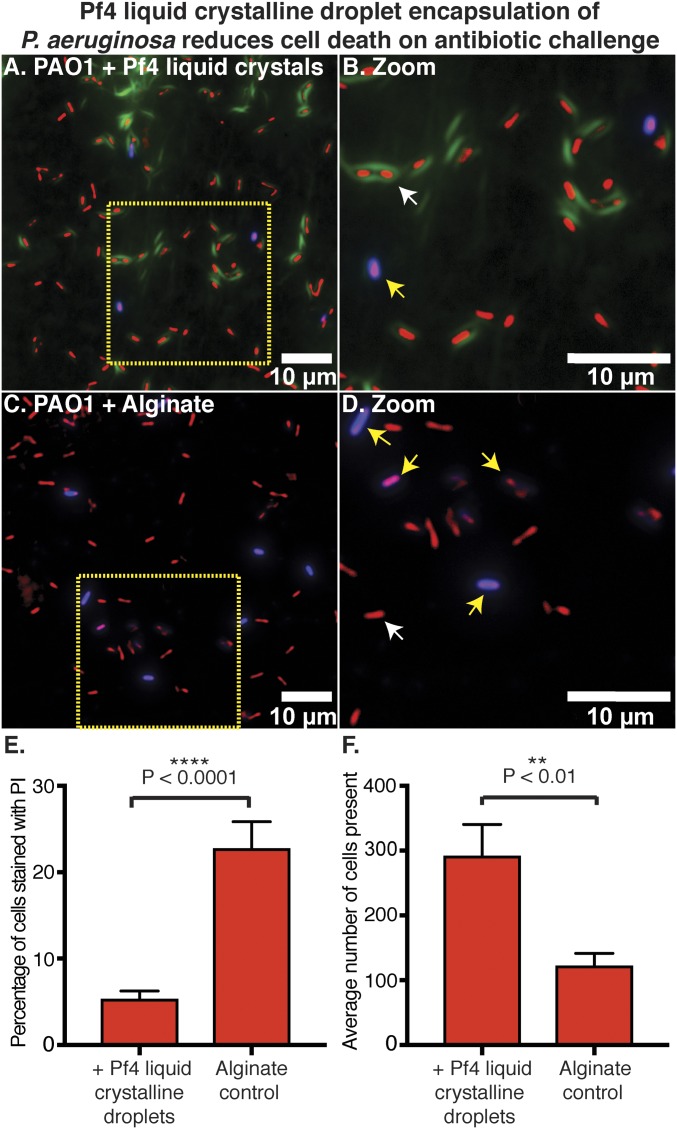
Fig. 6.
Pf4 liquid crystalline droplet encapsulation of P. aeruginosa prevents cell death on antibiotic treatment. (A) Optical microscopy of the antibiotic protection assay presented in Fig. 4, containing P. aeruginosa cells, alginate, Pf4, and tobramycin (Fig. 4A, bar 4) stained with PI. Bacteria are shown in red (pseudocolor of transmitted light channel), Pf4 liquid crystalline droplets in green, and PI staining in blue. (B) Zoom of A shows Pf4 liquid crystalline droplet encapsulated bacteria are not stained with PI (live cells indicated by white arrows and dead cells indicated by yellow arrows). (C) Optical microscopy of the condition lacking Pf4 filaments from the antibiotic protection assay presented in Fig. 4, containing P. aeruginosa cells, alginate, and tobramycin (Fig. 4A, bar 3) stained with PI. (D) Zoom of C shows staining of cells with PI. All fluorescence images were background subtracted. (E) Bar chart showing quantitation of PI staining with the percentage of cells stained with PI (y axis) in the presence or absence of Pf4 liquid crystalline droplets (x axis). (F) Bar chart showing the average number of cells observed per image, in randomly collected fields of the sample (y axis) in the presence or absence of Pf4 liquid crystalline droplets (x axis). Mean values are shown and the error bars denote SE. Experiment was performed in triplicate (n = 30 images).