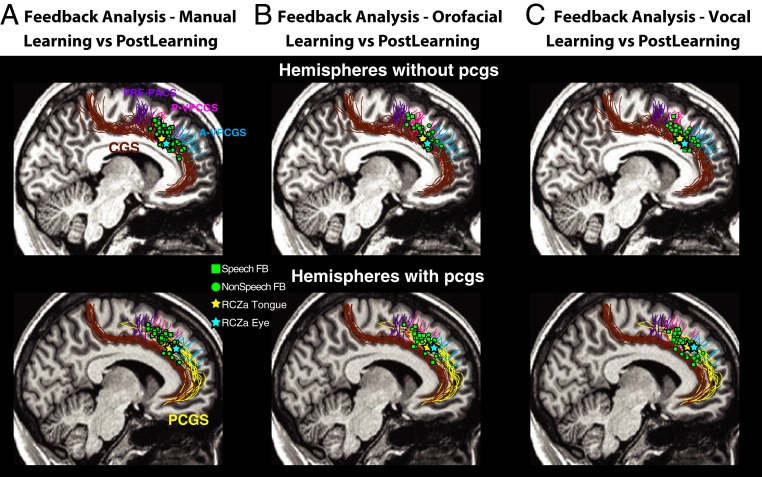
Fig. 6.
MCC activations associated with auditory vocal feedback (FB) analysis in relation to the face motor representation of the anterior rostral cingulate motor zone (RCZa). Comparison between the BOLD signal at the occurrence of speech (squares) and nonspeech (circles) feedback during conditional associative learning versus postlearning in individual subjects (each square/circle represents the location of increased activity of one subject) and in hemispheres displaying both a cingulate sulcus (cgs) and a paracingulate sulcus (pcgs; Top) and in hemispheres without a pcgs (Bottom). (A) Activations in the manual condition. (B) Activations in the orofacial condition. (C) Activations in the vocal condition. Green squares and circles correspond to speech and nonspeech feedback, respectively. Yellow and blue stars represent average locations of the tongue and eye motor representations in the RCZa that were derived from a motor mapping task in ref. 31. Abbreviations: cgs, cingulate sulcus; pcgs, paracingulate sulcus; prepacs, preparacentral sulcus; a/p-vpcgs, anterior/posterior vertical paracingulate sulcus.