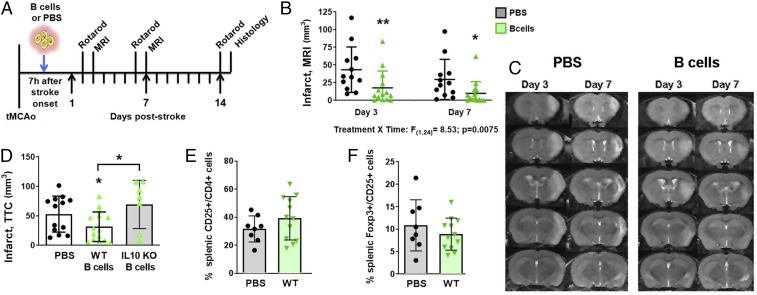
Fig. 1.
B cell adoptive transfer reduces infarct volumes via IL-10 but independently of immunomodulation. (A) Experimental timeline for B cell adoptive transfer 7 h after tMCAo. (B) Infarct volumes quantified from (C) serial MR images show that naïve B cells (green upward triangles) significantly decrease infarct volumes 3 and 7 d poststroke as compared to PBS control (black circles). (D) B cells isolated from wild type (WT) B6 mice (solid green triangles, white bar) and IL-10 KO mice (open green triangles, gray bar) show that only WT B cells reduced infarct volumes 3 d after tMCAo compared to PBS controls (black circles; determined by one-way ANOVA). (E) WT B cell treatment did not differentially activate CD4+CD25+ T cells in the spleen, nor did they (F) induce a regulatory T cell population in the spleen. Significance determined by two-way repeated-measure ANOVA or Student’s t test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. PBS control unless indicated by bracket).