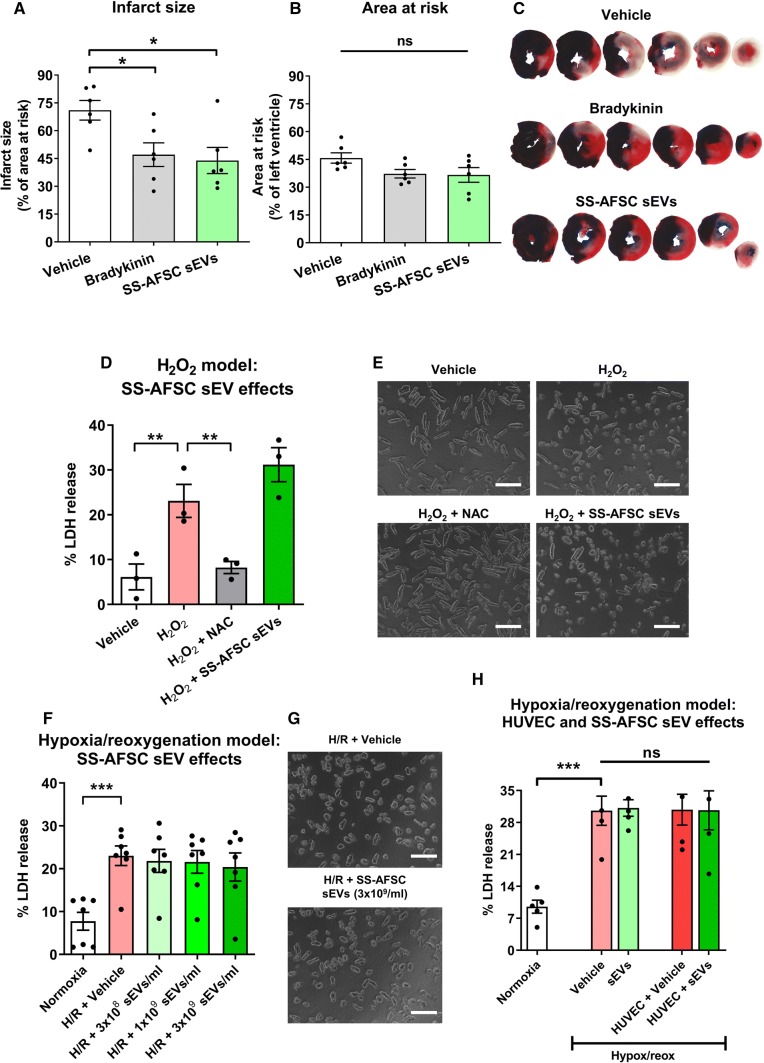
Fig. 4.
Effects of SS-hAFSC sEVs on cardioprotection in vivo and in vitro. a Infarct size as a percentage of the area at risk (ischaemic area) in a rat ischaemia–reperfusion injury model. Vehicle (PBS), Bradykinin (40 µg/kg), or SS-hAFSC sEVs (2 × 1011 particles/rat) were administered intravenously, 2 min prior to reperfusion. n = 6. *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test. b Area at risk as a percentage of left ventricle area. n = 6. p > 0.05, one-way ANOVA. c Representative images of a and b. d, e H2O2-induced death of primary cardiomyocytes treated with 40 µM H2O2 and Vehicle (water, PBS), N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC, 300 µM), or SS-hAFSC sEVs (1 × 1010 particles/ml). Cell death was assessed by LDH release. **p < 0.01, one-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test. n = 3. Representative images are shown on e. Scale: 200 µm. f, g Hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced death of primary cardiomyocytes in the absence or presence of SS-hAFSC sEVs. Cell death was assessed by LDH release. ***p < 0.001, one-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test. n = 7. Representative images are shown on g. Scale: 200 µM. h Effects of the stable sEV-treated HUVEC secretome in the hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte death model. Primary cardiomyocytes were treated with non-conditioned (Vehicle or sEVs at 1 × 1010 sEVs/ml) or HUVEC-conditioned medium (vehicle-treated: HUVEC + Vehicle, or sEV-treated: HUVEC + sEVs at 1 × 1010 sEVs/ml). ***p < 0.001, ns non-significant, one-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. n = 5