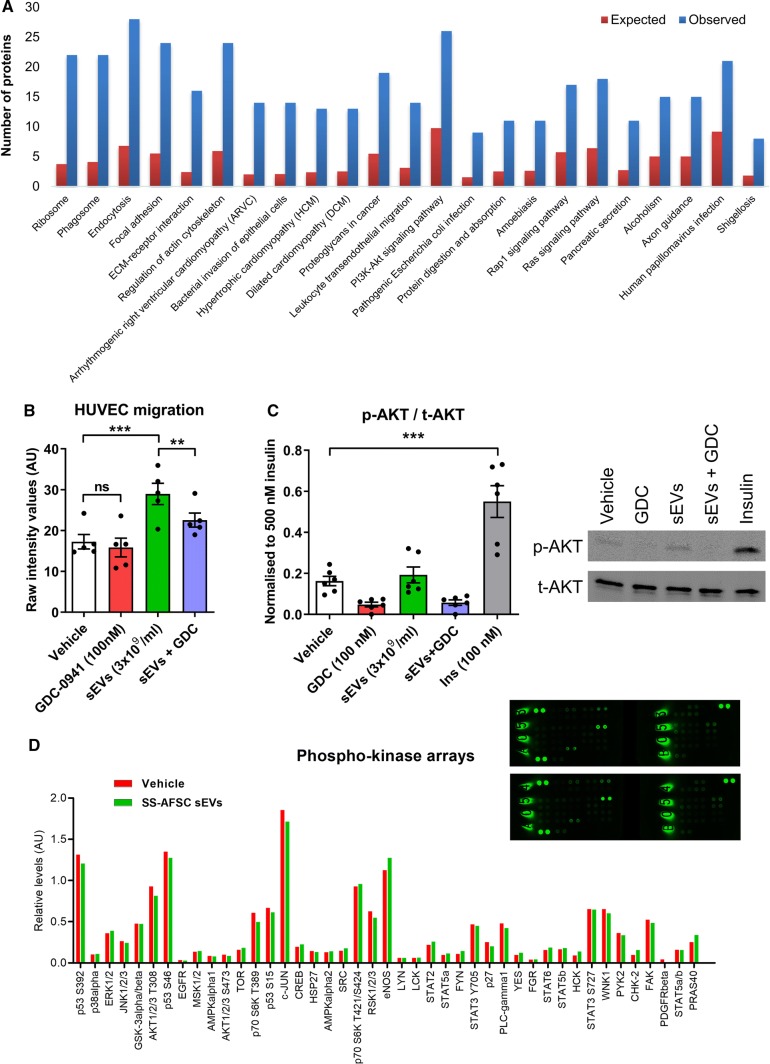
Fig. 8.
Mechanism of SS-hAFSC sEV-induced endothelial cell migration. a Proteomic analysis of SS-hAFSC sEV-enriched proteins (> 1.5 times) and SS-hAFSC sEV-exclusive proteins was performed. Overrepresented KEGG pathways are shown ranked by their p values for enrichment. Red bars—expected number of proteins (based on the number of proteins in the human proteome); blue bars—observed number of proteins. b HUVEC migration in response to SS-hAFSC sEVs and vehicle (PBS, DMSO) or PI3K pathway inhibitor (GDC-0941). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns non-significant (p > 0.05), one-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. n = 5. c Western blotting results for total and phosphorylated AKT in endothelial cells. HUVECs were incubated with Vehicle (PBS, DMSO), GDC-0941, SS-hAFSC sEVs, SS-hAFSC sEVs + GDC-0941 or insulin (control) for 15 min. Results are presented relative to 500 nM insulin control. ***p < 0.001, one-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. n = 6. Representative images shown on the right. p-AKT: phosphorylated AKT, t-AKT: total AKT. d Phospho-kinase array for detection of phosphorylated kinases/kinase targets in endothelial cells. HUVECs were incubated with vehicle (PBS) or SS-hAFSC sEVs (1 × 1010 particles/ml) for 15 min. Results are presented relative to control proteins. Images of the membranes shown in the top right corner: Vehicle (top, A053 and B053) and SS-hAFSC sEVs (bottom, A054 and B054)