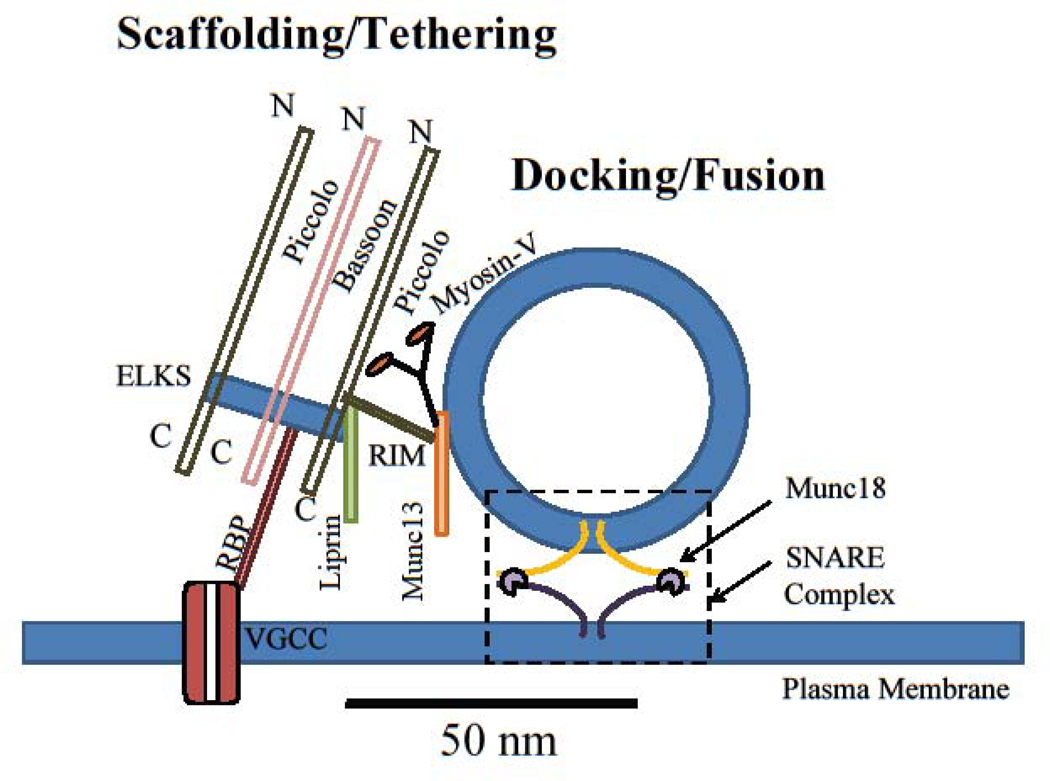
Figure 1: The spatial organization of proteins at release sites of the active zone.
Scaffolding proteins (Piccolo, Bassoon, ELKS, Liprin-α, etc) organize individual release sites. Tethering and docking proteins (RIM1/2, Munc13, myosin V, Munc18, etc) orchestrate assembly of release machinery and synaptic vesicle docking at the release sites. Release machinery (SNAREs, synaptotagmins, etc) mediate synaptic vesicle fusion with the plasma membrane to release neurotransmitter. Dashed box represents the vesicle docking/fusion area at which the SNARE complex formation occurs. VGCC: voltage-gated calcium channels; RBP: RIM binding protein; N: N terminus; C: C terminus.