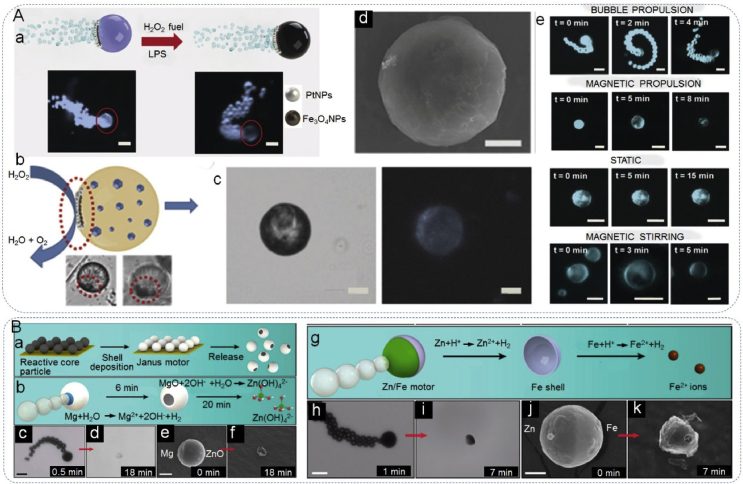
Fig. 14.
Janus particles constructed self-propelled motors. (Aa) Bubble propulsion and optical microscopy images of the Janus micromotors before and after the addition of the lipopolysaccharide, (Ab) asymmetry and Janus character of the micromotors, (Ac) optical microscopy image showing the structure of the micromotors and corresponding fluorescence image, (Ad) SEM image of micromotors, (Ae) time-lapse microscopy images showing the fluorescence intensity of moving and static micromotors. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [53]. Copyright 2017, Wiley-VCH. (Ba) Fabrication of Janus micromotors: particles were spread on a glass substrate followed by sputtering of shell materials and release, (Bb) design of Mg/ZnO Janus micromotors, (Bc and Bd) microscope images of the propulsion and degradation of a typical Mg/ZnO Janus micromotor in 0.5 M NaHCO3 solution at 0.5 and 18 min, respectively, (Be and Bf) SEM images of two typical Mg/ZnO Janus micromotors in 0.5 M NaHCO3 solution at 0 min (unreacted) and 18 min, respectively, (Bg) design of Zn/Fe Janus micromotors, (Bh and Bi) microscope images of the propulsion and degradation of a typical Zn/Fe Janus micromotor in simulated gastric acid at 1 and 7 min, (Bj and Bk) SEM images of two typical Zn/Fe Janus micromotors at reaction times of 0 min (unreacted) and 7 min, respectively. Scale bars for Bc-Bf, Bh, Bi, 20 μm; for Bj and Bk, 5 μm. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [54]. Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society.