Figure 7.
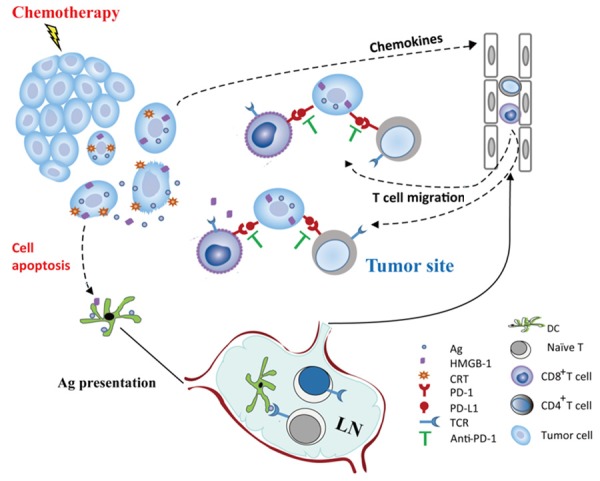
The potential synergistic mechanism of optimal dose platinum chemotherapy and PD-1 antibodies in cancer prevention. Platinum chemotherapeutic agents induced tumor cell apoptosis, and the stressed tumor cells released immunogenic signals (such as CRT and HMGB1). These signals allowed dendritic cells, the essential antigen presenting cells of the innate immune system, to take up portions of the stressed tumor cells and then presented tumor antigen to cognate T cells. Tumor antigen specific T cells with PD-1 expression are activated in lymph nodes and recruited to the tumor site. Unfortunately, in the tumor microenvironment, the PD-L1 molecule, which is expressed on the surface of tumor cells, engages with PD-1 on recruited T lymphocytes and blocks T cell function. Effective blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway interferes with the immune evasion of tumor cells and allows the immune system to control residual tumor cells.
