Figure 5.
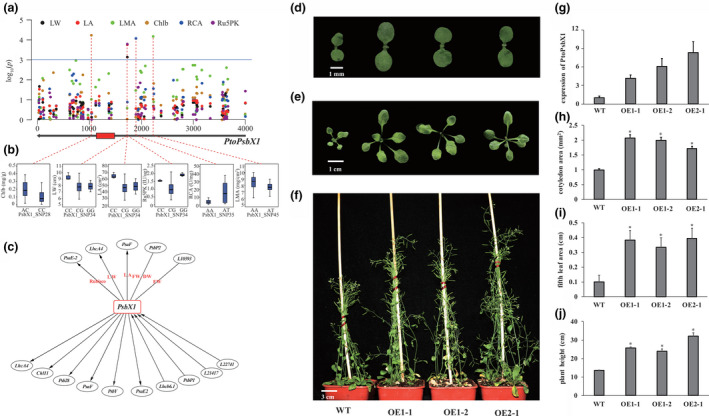
PtoPsbX1 is a hub gene that functions as an important genetic regulatory factor underlying the photosynthetic pathway in P. tomentosa. (a) Manhattan plot displaying the association results between all SNPs of PtoPsbX1 and six photosynthetic traits. The gene structure is shown below the plot (red rectangle, coding sequences; black lines, noncoding sequences). (b) Box plots showing the genotype effects of each significant SNP of PtoPsbX1 and its associated traits. (c) PtoPsbX1 functions as a ‘connector’ linking nine PEGs and three lncRNAs by epistasis and eQTNs in the photosynthetic pathway. The ellipses at the top represent genes that interact with PtoPsbX1 with epistatic effects underlying photosynthetic traits. The ellipses at the bottom represent gene interactions within eQTNs. The arrows pointing to PtoPsbX1 indicate genes that regulate the expression of PtoPsbX1; the arrows pointing to other genes indicate that PtoPsbX1 regulates the expression of the PEGs. (d‐f) Morphological comparison of OE‐PtoPsbX1 lines and the wild type (WT). (g) Relative expression levels of PtoPsbX1 and plant height in four OE‐PtoPsbX1 lines and the WT. (H–J) Quantitative measurement of cotyledon area (h), area of the fifth rosette leaf (i) and mature plant height (j) in the A. thaliana lines. *Significant differences from the WT based on Student’s t‐test (P < 0.01); n = 15.
