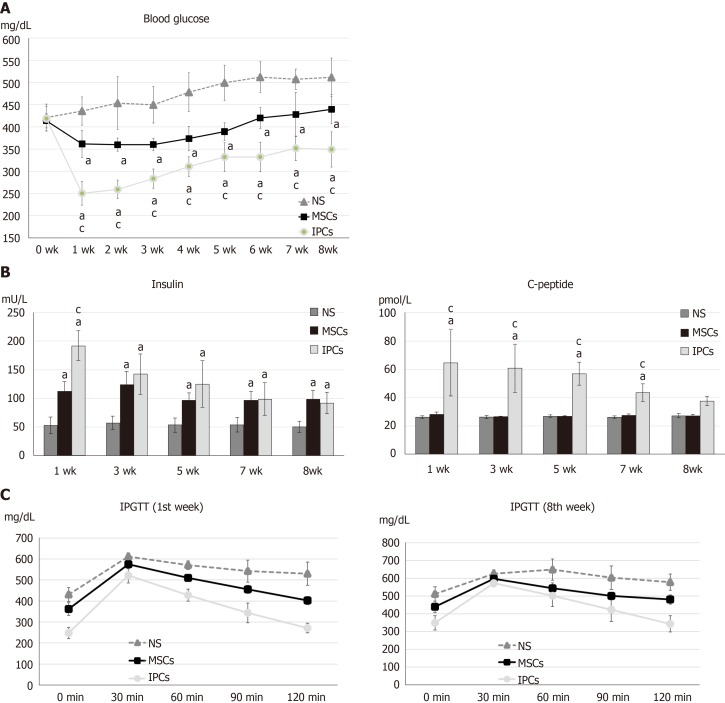
Figure 3.
Comparison of differences in blood glucose, serum insulin, serum C-peptide, and intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test results between streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats treated with undifferentiated human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells and insulin-producing cells. A: aP < 0.05, compared to the normal saline (NS) treatment group, the rats in the two treatment groups had significantly decreased blood glucose levels; cP < 0.05, blood glucose levels in rats in the insulin-producing cell (IPC) group were significantly lower than in rats from the undifferentiated human Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cell (hWJ-MSC) group; B: aP < 0.05, compared to the NS treatment group, the rats in other two treatment groups had significantly higher serum insulin levels; cP < 0.05, serum insulin levels in rats from the IPC group were significantly higher than those in rats from the undifferentiated hWJ-MSC group; aP < 0.05, compared to the NS treatment group, rats in the IPC treatment group had significantly higher serum C-peptide levels; cP < 0.05, serum C-peptide level blood glucose level of rats from the IPC group was significantly higher than those in rats from the undifferentiated hWJ-MSC group; C: IPC and MSC treatment led to better improvement in the intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT) result than NS treatment in both the first and eighth weeks.