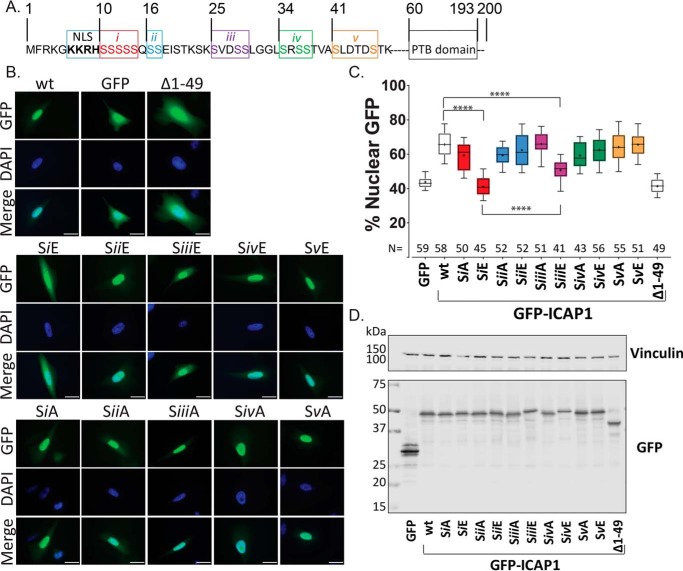
Figure 2.
Grouped phospho-mimicking mutants inhibit ICAP1 nuclear localization. A, schematic of ICAP1 noting the boundaries of the NLS sequence, PTB domain, and indicating the five groups (i–v) of serines that were mutated to glutamic acid or alanine. B, representative images of CHO cells expressing WT GFP-tagged ICAP1, or various ICAP1 mutants, fixed 24 h after plating on fibronectin and stained with DAPI (to identify nuclei). Bar, 10 μm. C, the percentage of the total integrated whole-cell GFP intensity found in the nucleus was calculated for each cell using CellProfiler 2.1. The total number of cells (N) in each condition from three independent experiments is indicated. Boxes, 25–50th and 50–75th percentile; whiskers, 10–90th percentile; dots, mean. Statistical significance was determined by a one-way ANOVA with Fisher's LSD test with multiple comparisons. ****, p ≤ 0.0001. D, representative immunoblots indicate expression of individual phosphomutants at the expected size; immunoblotting was against GFP for phosphomutants and vinculin for loading control. Uncropped immunoblots are shown in Fig. S1A.