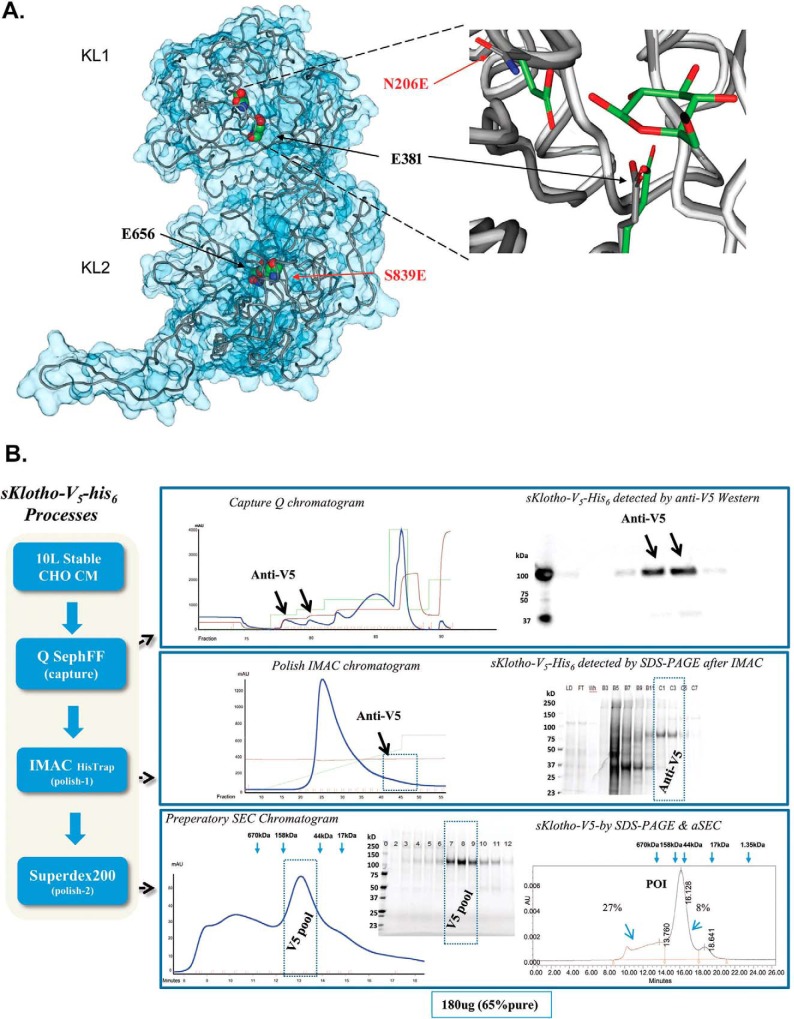
Figure 9.
Production of the enzyme-up EE mutant in which two catalytic glutamic acid residues conserved across the glycosidase family members were introduced into sKlotho. A, modeling of sKlotho EE mutant. The Klotho structure (5W21) (32) with active site residues was rendered in a space-filling model (CPK). Mutated residue numbers are indicated in red. The right part of the image is the overlay of the KLrP (2E9L, white peptide backbone and green side chain/ligand carbons) and KL1 (5W21, gray peptide backbone side-chain carbons) active site. B, purification of sKlotho EE mutant from stable CHO production. The sKlotho EE mutant was expressed in stable CHO cells, and conditioned medium was purified as described under “Experimental procedures”. Bio-Rad gel filtration standards (thyroglobulin (bovine, 670 kDa), γ-globulin (bovine, 158 kDa), ovalbumin (chicken, 44 kDa), myoglobin (horse, 17 kDa), and vitamin B12 (1.35 kDa)) are indicated by blue arrows.