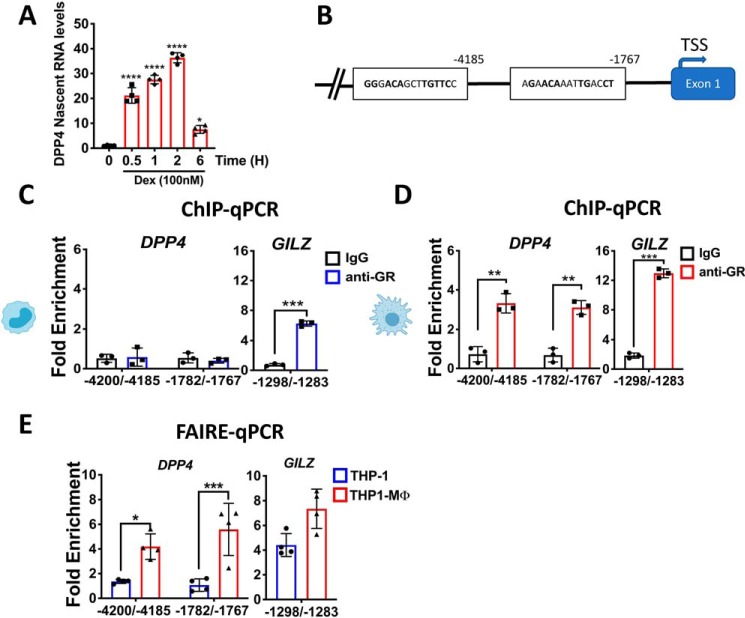
Figure 4.
Glucocorticoids regulate DPP4 expression by binding to GREs in the DPP4 promoter. A, quantitative real-time PCR analysis of DPP4 nascent mRNA from macrophage-like THP-1 cells (THP1-MΦ) that have been treated with 100 nm Dex for the indicated times. Dex treatment stimulates the transcription of a significant amount of DPP4 nascent mRNA within 30 min following Dex exposure. B, schematic representation of a fragment of human DPP4 gene that highlights two identified GREs located at positions −4,200/−4,185 and −1,782/−1,767 from the transcription start site (TSS). Monocyte-like THP-1 cells (C) and THP1-MΦ (D) were treated with or without 100 nm Dex for 2 h to evaluate by ChIP-qPCR the amount of GR bound to DPP4 GREs exclusively in THP1-MΦ. GR-ChIP samples were analyzed by quantitative PCR, and the Ct values of each experimental group were analyzed in triplicate, compared with their respective inputs, and normalized to the IgG isotype control. GR recruitment to DPP4 GREs is expressed as -fold enrichment of Dex- versus vehicle-treated cells. C and D, ChIP-qPCR of GR-bound GRE located in the promoter region of GILZ gene was used as positive control. E, chromatin remodeling was measured by FAIRE-qPCR to evaluate GR accessibility to the GREs in the DPP4 gene and GILZ gene (as control) in response to the monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation process. For each GRE, chromatin accessibility was determined and compared with the respective DNA input. Data are mean ± S.D. (error bars) and are representative of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001. Shown are a one-way ANOVA test with Tukey's multiple-comparison test (A) and a two-way ANOVA test with Sidak's multiple-comparison test (C–E).