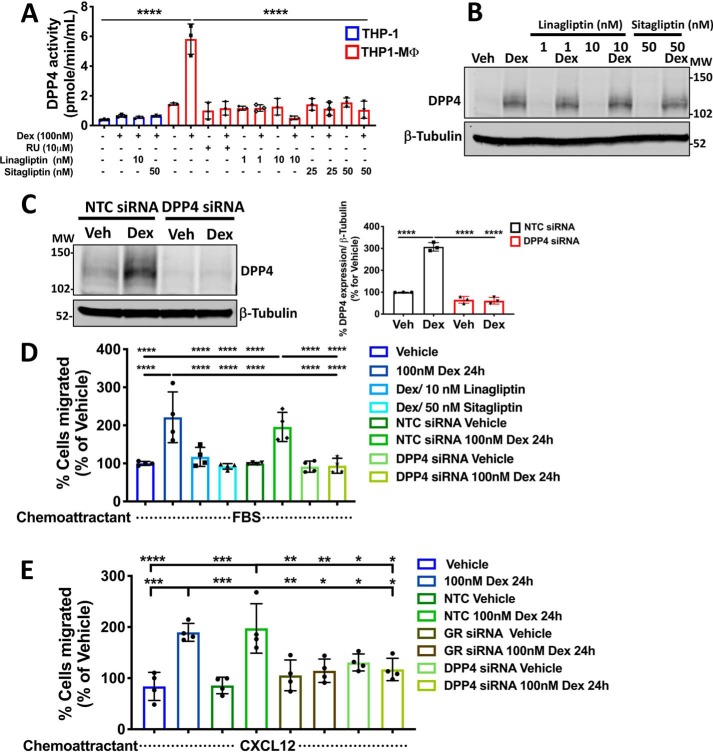
Figure 5.
The cell migration induced by dexamethasone in macrophage-like THP-1 cells is mediated through DPP4 activity. A, the enzymatic activity of DPP4 measured by fluorometric assay and induced by Dex was completely blocked by the DPP4 inhibitors sitagliptin (25 and 50 nm) and linagliptin (1 and 10 nm) in MΦ-THP-1. B, Western blotting for DPP4 showing that both DPP4 inhibitors do not affect the Dex-induced DPP4 protein expression. C, THP1-MΦ were transfected with NTC or DPP4 siRNAs. 24 h after transfection, cells were treated with or without Dex for 24 h, and DPP4 protein knockdown was evaluated by Western blotting (>70% reduction). On the left, a representative immunoblot of DPP4 and β-tubulin expression is shown. On the right, densitometry analysis of DPP4 normalized to β-tubulin is shown. D, Dex-induced THP1-MΦ migration is mediated by DPP4 expression. An in vitro migration assay shows that both pharmacological inhibition of DPP4 enzymatic activity, by linagliptin and sitagliptin, and silencing of DPP4 expression block the spontaneous migration of THP1-MΦ induced by Dex treatment. E, CXCL12-induced THP1-MΦ migration was blocked by GR and DPP4 knockdowns of cells following Dex treatment. Data are mean ± S.D. (error bars) and are representative of 3–4 independent experiments. ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA statistical test with Tukey's multiple-comparison test.