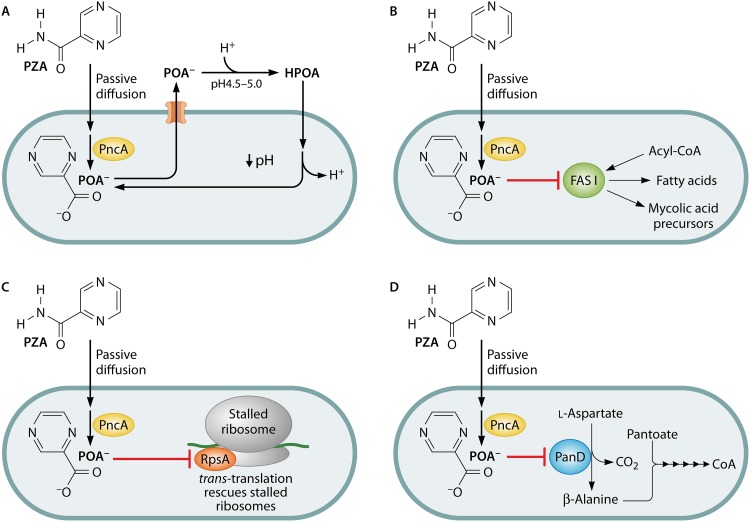
FIG 1.
Proposed modes of antitubercular action of pyrazinamide. Pyrazinamide enters the cell by diffusion and is activated by the cytoplasmic pyrazinamidase/nicotinamidase PncA. Pyrazinoic acid has been proposed to act as a protonophore leading to the acidification of the bacterial cytoplasm (A), an inhibitor of fatty acid synthase I (B), an inhibitor of trans-translation (C), and/or an inhibitor of coenzyme A biosynthesis (D).