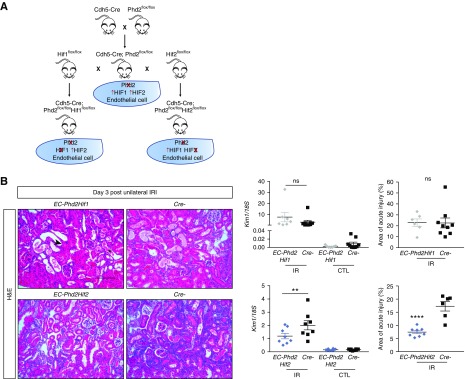
Figure 3.
Inactivation of endothelial Phd2 attenuates ischemic kidney injury through HIF-1 but not HIF-2. (A) Schematic view of crossbreeding between Cdh5-Cre transgenic mice and mice carrying conditional alleles for Phd2, Hif1α, or Hif2α leading to the generation of double mutants lacking either endothelial PHD2 and HIF-1 (EC-Phd2Hif1) or PHD2 and HIF-2 (EC-Phd2Hif2). (B) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)–stained sections of injured kidneys from EC-Phd2Hif1, EC-Phd2Hif2 mutants or their Cre- littermate controls 3 days after unilateral renal IRI. Arrow points to a dilated tubule; asterisk indicates a tubule with cast formation. Middle panels show Kim1 mRNA levels in IR and CTL kidneys (n=7–9 for Phd2Hif1 versus Cre-, P=0.14; n=8 for Phd2Hif2 versus Cre-, P=0.009; one-way ANOVA with Sidak correction for multiple comparisons). Right panels demonstrate scoring of acute injury, expressed as the percentage of kidney area affected in postischemic kidneys from EC-Phd2Hif1, EC-Phd2Hif2 mutants or their Cre- controls (n=6–9 for Phd2Hif1 versus Cre-, P=0.97; n=8–6 for Phd2Hif2 versus Cre-, P=0.009; two-tailed t test). Error bars represent SEM. **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001. Scale bar, 100 μm. CTL, contralateral kidney; IR, kidney subjected to unilateral IRI.