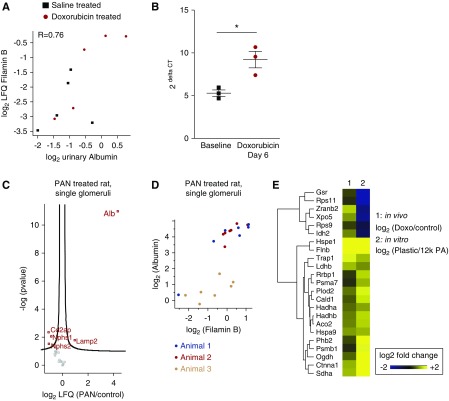
Figure 5.
Filamin-B abundance increases with proteinuria in animals and single glomeruli and is altered by mechanical stress. (A) Correlation analysis revealed a strong positive correlation of podocyte Filamin-B protein with urinary albumin concentration (R, Pearson’s correlation coefficient; P<0.05). (B) Quantitative PCR of glomeruli isolated from Doxorubicin-treated mice revealed a significant increase of Filamin-B mRNA levels (2ΔCT) upon injury. Filamin-B levels are normalized to HPRT. t test: *P<0.05. (C) Volcano plot of PAN-treated single rat glomeruli reveals a significant increase of albumin (Alb), whereas podocyte-specific proteins such as Nphs2 and Nphs1 are downregulated. (D) Correlation analysis of Filamin-B levels with albumin reveals a positive correlation, R=0.76. (E) Comparison of protein abundance in our Doxorubicin-treated podocytes with cell culture podocytes exposed to increased mechanical stress (when grown on plastic as opposed to 12-kPa soft matrices) revealed similar signatures with regard to mechanosensation.