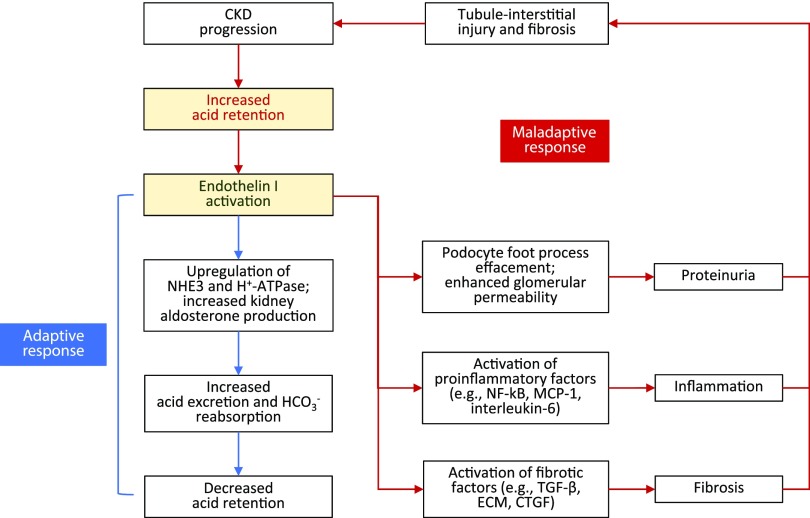
Figure 3.
ET-1: benefits and consequences. ET-1 is activated in response to metabolic acidosis. Increased intrakidney ET-1 stimulates NHE3-mediated Na+-H+ exchange and increases aldosterone activity in the kidney which increases acid excretion. This short-term response can become maladaptive with continual acid exposure, because sustained intrakidney ET-1 production is linked with proteinuria, inflammation, and fibrosis, which together promote further tubule-interstitial injury and worsening CKD. CTGF, connective tissue growth factor (CCN2); ECM, extracellular matrix; HCO3−, bicarbonate; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; NF-κΒ, nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells.