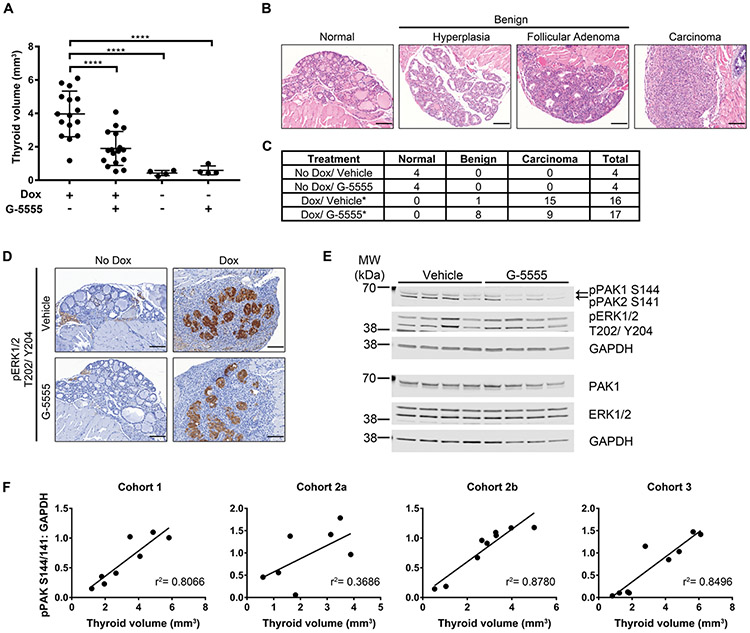
Fig. 7. In vivo effects of G-5555 in a BRAFV600E-inducible thyroid cancer mouse model.
BRAFV600E was induced in mouse thyroids by doxycycline-enriched chow for one week at the same time as G-5555 or vehicle oral gavage. Thyroids were harvested and volume (A) of one lobe was measured ex vivo. Comparisons among treatments were made by one-way ANOVA followed by Holm’s procedure. Data are represented as individual plots with means ± SD. ****P ≤ 0.0001 (B) Representative H&E images of the thyroid pathologies observed. Scale bar = 100 μm. (C) Number of mice in each treatment group with the observed pathologies. Carcinoma incidence between Dox/Vehicle and Dox/G-5555 were compared using a Fisher’s exact test. *P ≤ 0.05. (D) Representative pERK1/2 T202/Y204 IHC images showing induction of BRAFV600E in the thyrocytes with Dox. Scale bar = 100 μm. (E) Western blot of Cohort 1 mouse thyroid lysates. Each lane is lysate from an individual mouse treated with Dox and Vehicle or G-5555, as indicated. GAPDH is used as the loading control for the membrane above it. (F) Comparison of thyroid volume and quantification of the pPAK1/2 S144/141 western blot bands normalized to GAPDH for each western blot membrane. Each cohort of mice was treated at different times and the lysates from mice in Cohort 2 were divided on two gels (a and b), as titled. Comparisons were fit with a linear regression and the r2 values are shown.