Figure 5.
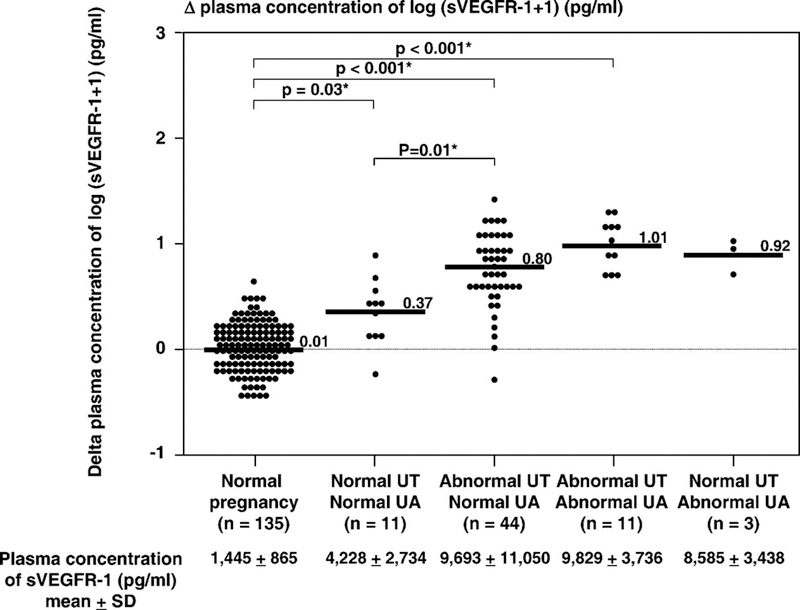
The mean delta plasma concentrations of normal pregnant women and patients with preeclampsia (n=69) sub-classified according to the results of uterine and umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry. Patients with preeclampsia who had abnormalities in both the uterine and umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry had the highest mean delta plasma sVEGFR-1 concentration (mean ± SD: 1.01 ± 0.22) among all groups. Patients who had normal Doppler velocimetry in both uterine and umbilical arteries had the lowest mean delta plasma sVEGFR-1 concentration (mean ± SD: 0.37 ± 0.31; ANOVA; p < 0.001). Patients with abnormal uterine, but normal umbilical artery, Doppler velocimetry had a mean delta plasma sVEGFR-1 concentration higher than normal pregnant women (mean ± SD: 0.80 ± 0.40 vs. mean ± SD: 0.01 ± 0.21; p<0.001; ANOVA post hoc Dunnett’s T3). The means ± SD of plasma sVEGF-R1 concentrations in each group are displayed in the figure. *p < 0.05.
