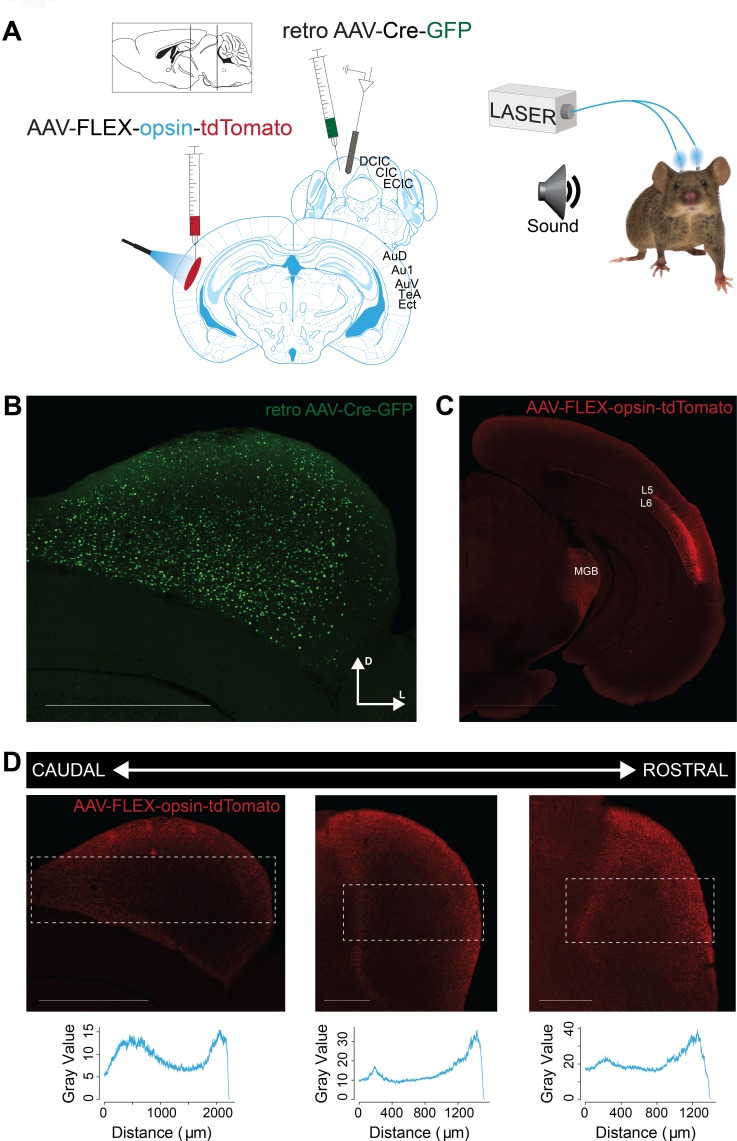
Figure 1. Opsin expression in corticocollicular feedback.
(A) Experimental design: To yield selective labeling of auditory cortico-collicular projections, a retroAAV-Cre-GFP construct is injected into the IC and AAV-FLEX-opsin-tdTomato construct is injected into the AC bilaterally. Recordings are made in multiple bilateral locations of the IC (left) of awake mice. Cannulas are implanted bilaterally in the auditory cortex, and a green/blue laser is used to silence/activate the cortico-collicular pathway (right). (B) Expression of the retro AAV-Cre-GFP construct in the IC. Scale bar: 1000 μm. (C) Selective expression of the AAV-FLEX-opsin-tdTomato construct in cell bodies in layer 5 (L5) and 6 (L6) of the AC that project to the IC. Fiber and terminal labeling is also present in the medial geniculate body, a known target of auditory cortico-collicular cells. Scale bar: 2000 μm. (D) Expression of the AAV-FLEX-opsin-tdTomato construct in fibers and terminals at multiple rostro-cadual levels of the IC. Expression, as measured by fluorescence intensity (bottom), is strongest in medial portions of the central nucleus of the IC and lateral portions of the external nucleus of the IC. Scale bar: left, 1000 μm; middle and right, 500 μm.