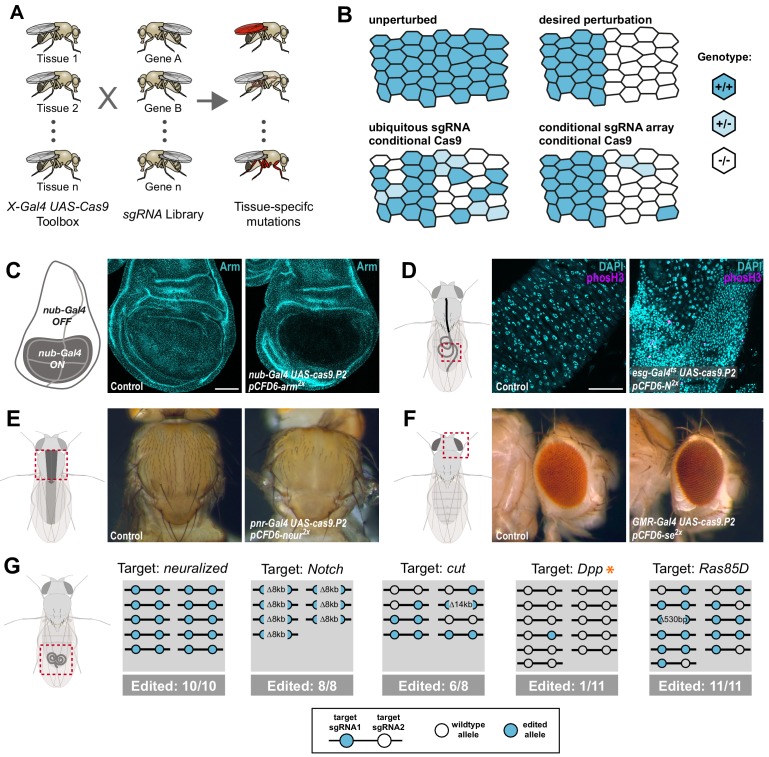
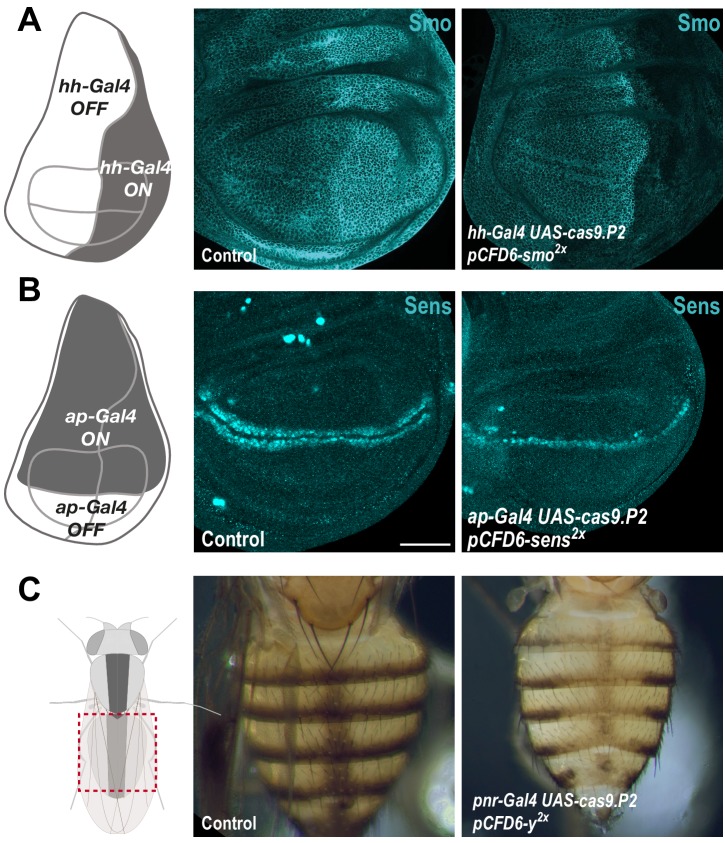
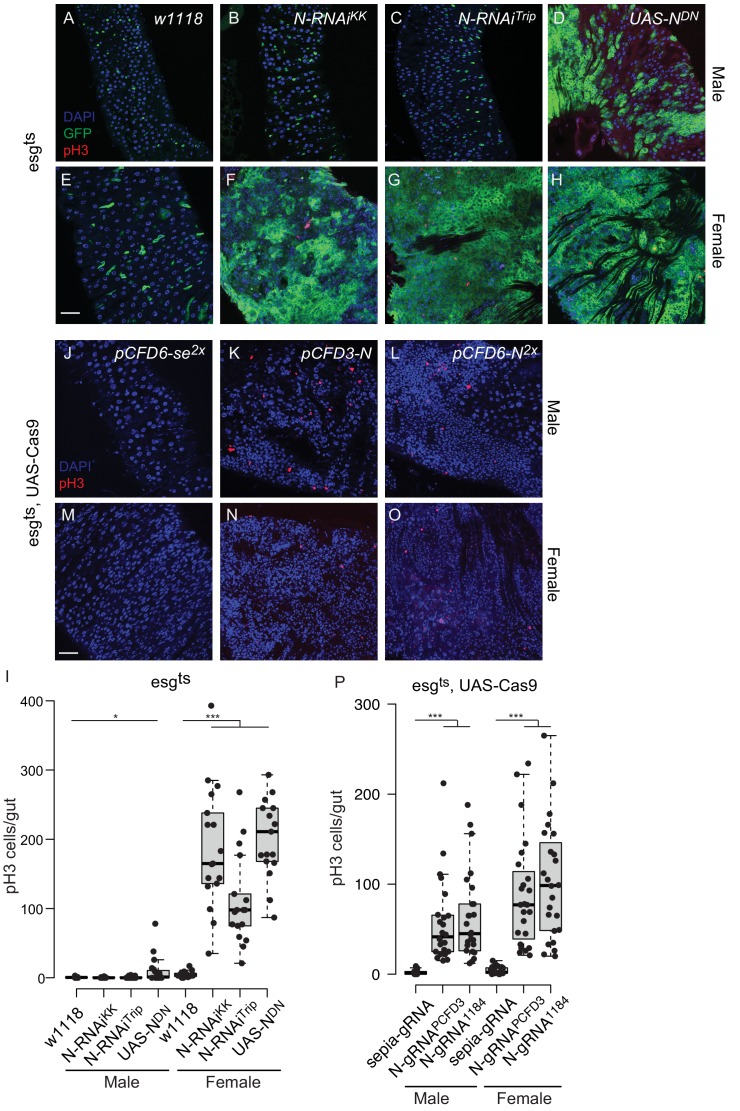
Figure 1. Conditional CRISPR mutagenesis with pCFD6 is robust across target genes and tissues.
(A) Schematic overview of the workflow. To perform tissue-specific targeted mutagenesis flies transgenic for a specific Gal4 driver (X-Gal4) and UAS-Cas9 are crossed to flies with a UAS-sgRNA transgene. Offspring from this cross express Cas9 and sgRNAs in Gal4 expressing cells, leading to mutagenesis of the target gene. (B) Schematic of gene editing outcomes typically observed with a single, ubiquitous sgRNA (lower left) or a conditional array of several sgRNAs (lower right). Leaky expression, that is expression in the absence of Gal4, from conditional Cas9 transgenes gives rise to ectopic mutagenesis in combination with ubiquitous, but not conditional, sgRNAs. Gene editing in tissues typically results in genetic mosaics, which can be enriched for bi-allelic knock-out cells through sgRNA multiplexing. (C) Conditional CRISPR mutagenesis in wing imaginal discs with nub-Gal4 in the wing pouch. Gene editing with pCFD6-arm2x results in loss of Arm protein exclusively in the Gal4 expression domain in nearly all cells. Control animals express the nub-Gal4 driver and UAS-cas9.P2. Scale bar = 50 µm. (D) Conditional CRISPR mutagenesis of Notch in intestinal stem cells drives tumor formation in the midgut. esgts (esg-Gal4 tub-Gal80ts) was used to repress expression of UAS-cas9.P2 and pCFD6-N2x until adult stages. Mutagenesis was induced for 5 days at 29°C and flies were returned to 18°C to avoid Cas9.P2 mediated toxicity. Posterior midguts 15 days after induction of mutagenesis are shown. esgts UAS-cas9.P2 pCFD6-N2x tissue shows an accumulation of stem cells (DNA marked in cyan) and an increase in mitotic cells (pHistone3 in magenta). Quantification of phenotypes are shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Control genotype is esgts UAS-cas9.P2 pCFD6-se2x. Scale bar = 50 µm. (E) Mutagenesis of neur in pnr-Gal4 UAS-cas9.P2 pCFD6-neur2x animals results in loss of thoracic bristles along the dorsal midline, where pnr-Gal4 is expressed. Note the tissue patch that retains bristles, reflecting mosaic mutagenesis. (F) Mutagenesis of the pigmentation gene se in the eye. GMR-Gal4 UAS-casp.P2 pCFD6-se2x animals develop a uniform dark eye coloration. Control animals in (E) and (F) express the respective Gal4 driver and UAS-cas9.P2 pCFD6-Sfp24C12x. (G) pCFD6 mediated mutagenesis in the germline. Shown is a summary of the mutational status at each sgRNA target site in individual F1 flies. nos-Gal4VP16 UAS-cas9.P1 pCFD6 flies expressing sgRNAs targeting the indicated essential genes are viable, demonstrating germline restricted mutagenesis, and transmit mutant alleles to their offspring. Shown is a summary of the mutational status at each sgRNA target site in individual flies. All lines, except the one targeting Dpp (asterisk), transmit mutant alleles to the majority of offspring. Flies expressing sgRNAs targeting Dpp in the germline produce few viable offspring and transmitted only a single, in-frame, mutation out of 11 analysed offspring. The same sgRNA construct results in highly efficient mutagenesis in somatic tissues (see Figure 4), consistent with haploinsufficiency of Dpp in the Drosophila embryo.