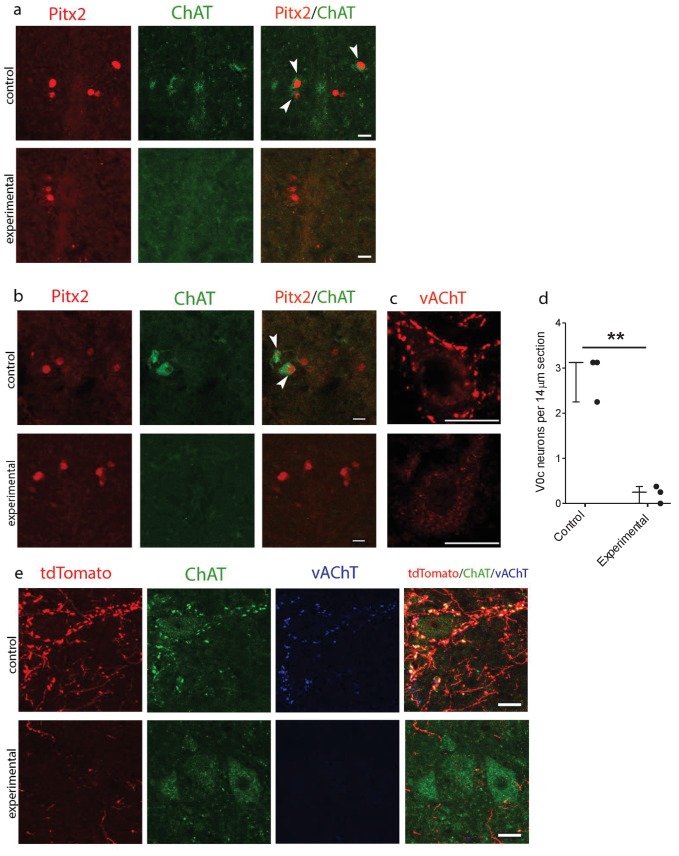
Figure 5. Genetic ablation of cholinergic Pitx2+ interneurons (V0c) eliminates C-boutons around motoneuron somata.
(a) Immunofluorescence in spinal cord sections of P2 wt (control) and Pitx2::Cre;vAChT-stop-DTA (experimental) mice using antibodies against Pitx2 (red) and Choline Acetyl Transferase (ChAT, green). (b) Immunofluorescence in spinal cord sections of P7 upper lumbar levels from wt (control) and Pitx2::Cre;;vAChT-stop-DTA (experimental) mice using antibodies against Pitx2 (red) and ChAT (green). White arrows in (a) and (b) point to double positive neurons. Neurons that are positive for cholinergic markers only but not positive for Pitx2 are preganglionics, typically present in the intermediate zone in these levels (a, b). (c) Immunofluorescence of motoneurons and their C-bouton terminals in upper lumbar spinal cord sections using an antibody against vAChT. (d) Average number of V0c neurons per 14 µm section in control and experimental P7 mice. (e) Immunofluorescence of motoneurons and their C-bouton terminals in upper lumbar spinal cord sections of P25 Pitx2::Cre;tdTomato (control) and Pitx2::Cre;tdTomato;vAChT-stop-DTA (experimental) mice using antibodies against tdTomato (red), ChAT (green) and vAChT (blue); Photos acquired with confocal microscopy using (a, b) 20x lens and (c, e) 40x lens. Sections thickness was 14 μm and scale bar is 20 µm; n = 3 mice for each condition; **p<0.01.