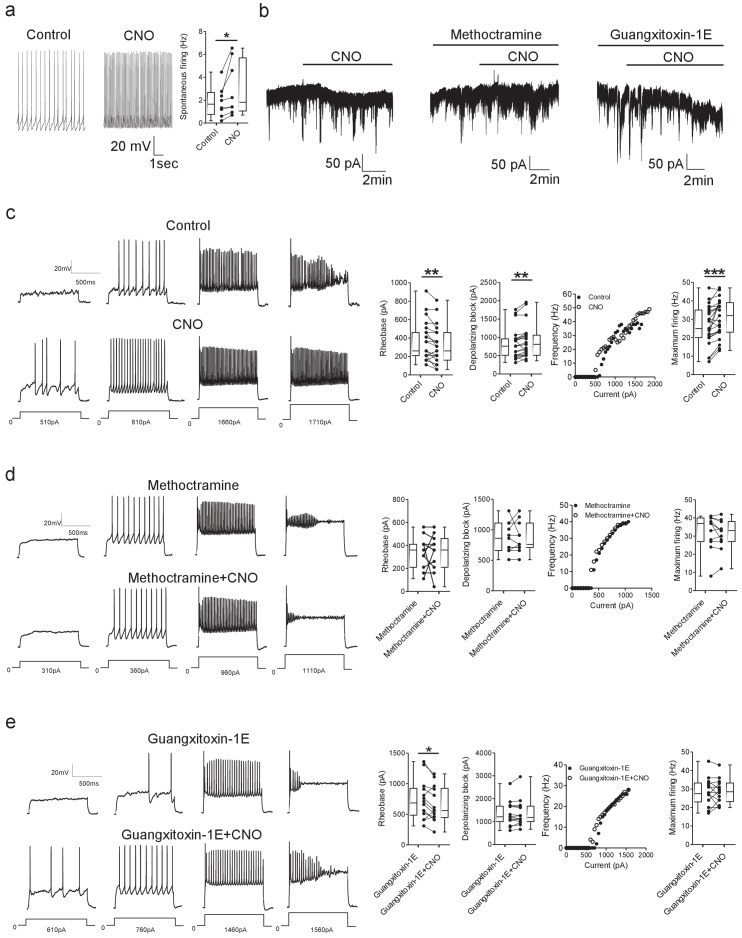
Figure 7. DREADD-based activation of Pitx2+ interneurons increases motoneuron firing via M2 receptors and Kv2.1 channels.
(a) Spontaneous firing of a Pitx2+ interneuron from a Pitx2::Cre;tdTomato;hM3Dq mouse in control conditions and during the application of CNO; along with firing frequency data pooled for all recordings (n = 8). (b) Representative traces illustrating changes in holding current (Vhold = −60 mV) during recordings of motoneurons in the presence of CNO alone (left) or co-applied with methoctramine (10 μM, middle) or guangxitoxin-1E (50 nM, right). (c) Motoneuron firing in response to current steps in control conditions and in the presence of CNO (left) with pooled data plotted to show changes in rheobase, depolarizing block, current-frequency relationships and maximum firing (right) (n = 23). (d, e) Examples of motoneuron firing and pooled data depicting firing parameters in the presence of methoctramine and methoctramine co-applied with CNO (d; n = 11) or Guangxitoxin-1E and CNO co-applied with Guangxitoxin-1E (e; n = 14). *p>0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.